|
Key Takeaways: |
|
- A dependable home emergency generator is essential for Australian homeowners, particularly those in remote places or regions prone to harsh weather. - Four main types of generators - powered by different substances - are popular options for creating an emergency power system: diesel, propane, natural gas, and solar generators. - An appropriately sized generator is one factor that makes up the best home generator. A 10kVA generator is sufficient for basic power usage during an outage. - We recommend the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus as the most suitable home backup generators for charging appliances and electronics during emergencies. |
Importance of Home Emergency Generator
Home emergency generators are increasingly becoming indispensable in many parts of the world. Storms, bushfires, heatwaves, and outdated electrical infrastructure contribute to Australia's increasing risk of power outages.
These disruptions are more than just a nuisance; they can jeopardise safety, cause considerable economic losses, and endanger vulnerable groups such as older people and those who rely on medical gadgets. They are continuously pressuring the ageing electrical grid, leaving you and your family without power for hours or even days.
A dependable home emergency generator is essential for Australian homeowners, particularly those in remote places or regions prone to harsh weather. Having power during an emergency might be crucial, whether you're managing medical equipment, keeping food from rotting in your refrigerator, or simply staying connected and informed. Home generators guarantee that lights and appliances remain operational during power outages, providing security and flexibility.
Types of Home Emergency Generators
The classification of emergency home generators is primarily based on three dimensions: fuel type, installation type, and technology type. Each dimension encompasses various kinds of generators, their attributes, and application scenarios.

Although other generator styles exist, powered by sources other than those listed here, there are various options on the market. Four main types of generators - powered by different substances - are popular options for creating an emergency power system: gasoline, diesel, propane, and natural gas.
Propane Generator
Propane generators are a fantastic choice if you're concerned about the potential emissions from your system. One of the negatives is that these generators can consume a lot of fuel quickly compared to other power sources.
Diesel Generator
Diesel systems consume less fuel and are portable. If you're concerned about cost, you will want to evaluate whether a generator is air or liquid. These cannot store diesel for a lengthy period but are quick and easy to start when needed.
Natural Gas Generator
Natural gas generators are larger models that require a natural gas connection run from the unit to the gas source. These standby types require less maintenance and do not need to be refuelled, contributing to their popularity.
Solar Generator
A solar generator is a portable power station that uses solar energy to recharge, offering an off-grid, renewable alternative to traditional generators. It combines a single unit's battery, inverter, and charge controller, allowing users to store solar energy and convert it into usable AC or DC power for various devices. Typically, they are recharged via solar panels and offer AC wall outlets and car charging options for added versatility.
|
Types of Generators |
Pros |
Cons |
Working Principle |
| Propane Generator |
Longer shelf life Can be connected to existing propane supply |
Costs Limited resources Pollution Noise |
Propane generators use a propane-powered internal combustion engine to drive an alternator. |
| Diesel Generator |
High fuel efficiency Long-lasting Lower operating costs |
Higher initial costs Higher noise Heavier Pollution Require maintenance |
Diesel generators employ a diesel-powered internal combustion engine. |
| Natural Gas Generator |
Lower cost Commonly used Easy to start Lighter than diesel |
Lower fuel efficiency Shorter shelf life Higher operating costs Pollution |
Gasoline generators use a gasoline-powered internal combustion engine to drive an alternator. |
| Solar Generator |
Renewable Portability Clean power Ease of use Off-grid power No maintenance Lower noise |
Limited power output Initial cost Battery capacity limitation |
It combines a battery, inverter, and charge controller in a single unit, allowing users to store solar energy and then convert it into usable AC or DC power. |
Home Emergency Generators by Installation Types
Home emergency generators fall into two main installation categories: portable generators, which offer flexibility and lower costs but require manual operation and refuelling, and standby generators, which are permanently installed for automatic whole-house power during outages, though at a higher upfront and installation expense.
Standby Generator
Standby generators, powered by natural gas, diesel, or propane, are typically large units installed at the back of a home. They start within seconds of a power outage and perform weekly self-tests.
Portable Generator
Portable home generators take up less space and may be placed out of the way when unused. They often power things or a transfer switch via an extension cord.
One disadvantage of a portable generator is that you must start it yourself. On the other hand, one of the advantages of a portable generator is that you can take it anywhere you need, such as on a camping trip or to a tailgating party for your favourite sports team. Portable generators frequently have a large fuel tank, outlets for plugging in various devices, and wheels.
|
Types of Generators |
Pros |
Cons |
Working Principle |
|
Standby Generator |
Automatic startup Reliable Low maintenance |
Large size Complex installation Higher cost Need enough space |
Connected to home's electrical system, automatically switches to backup power during outage. |
|
Portable Generator |
Compact Portable Versatile |
Manual start Shorter runtime Limited capacity |
Powered by the internal combustion engine, connected via extension cords or transfer switch |
Home Emergency Generators by Technology Types
Conventional generators produce AC power directly from the alternator at a constant engine speed, resulting in higher power output suitable for heavy-duty tasks but with fluctuating voltage and frequency, increased noise, and lower fuel efficiency. In contrast, inverter generators convert AC to DC and back to clean AC with a stable sine wave, allowing for quiet operation, fuel efficiency, and safe power for sensitive electronics.
Conventional Generator
Conventional generators use diesel, gas, or propane to convert mechanical energy into electricity. The motor and alternator generate an alternating current (AC) of 120 or 240 volts.
Inverter Generator
Inverter generators, available in sizes up to 50,000 watts, convert AC to DC voltage and then back to AC power, resulting in a quieter system. Conventional generators, on the other hand, are designed to run for long periods and are often louder due to their engines and mufflers.
Inverter generators are a safer option for powering sensitive home electronics due to their consistent energy flow and ability to produce only as much energy as needed. They can run for 8-10 hours and range in size from 1000 to 4000 watts.
|
Type |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Working Principle |
| Conventional Generator |
Long runtime Higher power output Typically more affordable |
Noisier operation Less fuel-efficient Power fluctuations |
Convert mechanical energy from engine to AC electricity using an alternator. |
| Inverter Generator |
Quiet operation Fuel-efficient Stable power output |
Smaller power output Shorter runtime Typically more expensive |
Convert mechanical energy to DC, then invert to stable AC using electronic circuitry. |
What Size Home Emergency Generator Do I Need?
Choosing an appropriate home emergency generator ensures that homes, businesses and critical infrastructure can maintain basic power needs during a hurricane.
For example, in Australia, many homes install medium-sized generators of 5kW to 10kW during the cyclone season. In summary, before selecting the right emergency generators for a cyclone, determine your power needs:

Step 1: List the appliances you need to power the generator.
Start by listing all the appliances you plan to power with the generator and their starting and running wattages, including essentials such as refrigerators, heaters or air conditioners. Some appliances may have a starting wattage requirement, usually 2 to 3 times the running wattage.
Appliances typically have a wattage number on the bottom, back or nameplate. If your appliance does not list this information, you can check the user manual or browse the manufacturer's website to find the wattage of a specific product.
The following table shows information on some common appliances' starting and running wattage.
|
Appliances |
Running Wattage |
Starting Wattage |
|
Circular Saw |
1500W |
1500W |
|
Ceiling Fan |
800W |
1200W |
|
Electric Stove |
1500W |
0W |
|
Heat Pump |
4700W |
4500W |
|
Iron |
1200W |
0W |
|
Microwave |
1000W |
0W |
|
Refrigerator |
800W |
1600W |
|
Sump Pump |
800W |
1200W |
|
Space Heater |
1600W |
0W |
|
Computer |
200W |
0W |
|
TV |
60W |
0W |
Step 2: Calculate the total power.
Calculate the total running power of all the devices you need to power, considering the device with the highest starting power. Add up the starting and running power of all the devices you need to power in step 1, and you will get the total power required.
Here is an example:
Suppose a refrigerator with a starting power of 1600W and a running power of 800W, four light bulbs with a running power of 75W, and a microwave oven are running together. How much power output is required for the emergency generator?
800W+ 1600W+ 75W*4+ 1000W= 3700W
After calculating the total power, please leave a certain margin to ensure the stability and security of the power system. (It is generally recommended to leave 20% of the total power as a margin)
3700W / (1-20%) = 4625W
So you need at least a 5kW emergency generator. Remember that the above data estimates are for reference only, and the actual power consumption of the appliances may vary.
Step 3: Common Sizes of Home Emergency Generators
An appropriately sized generator is one factor that makes up the best home generator. A generator that is too big or too small for your power needs can be inefficient and even cause damage to electrical systems. In contrast, a tiny generator can be unreliable and overheat.
To determine the size of a generator for a house, list all the appliances you want to power in case of an outage. Note they're starting and running watts to get an idea of the maximum and rated power output you should have. Calculate the total power in kW or k VA to estimate the power you need.
Recreation, power tools, small appliances, and lighting all need 500 to 3,000 watts.
Recreation, heating and cooling, and mid-size appliances use 3,100 to 6,000 watts.
6,100 to 10,000 watts for emergency power, heating and cooling, large appliances, and water heaters.
Emergency and whole-house power at 10,100 watts or higher.
A generator's output capacity is measured in kilo-volt-amperes (kVA). A 10kVA generator is sufficient for basic power usage during an outage, while a generator in the 50kVA to 70kVA range is recommended for larger homes. A 10-20kVA generator can suffice as a backup power source for a townhouse.

What Can an Emergency Generator Power?
A home emergency generator can provide the necessary power support for almost all key appliances and equipment to ensure the regular operation of basic life and work. The following is a detailed introduction to what appliances emergency generators can usually power in Australia:
|
Common Appliance Types |
Appliances |
|
Lighting Equipment |
LED lights, fluorescent lights, emergency lights, etc. |
|
Communication Equipment |
Mobile phones, walkie-talkies, radio communication equipment, etc. |
|
Kitchen Appliances |
Ovens, microwave ovens, coffee machines, refrigerators, etc. |
|
Refrigeration and Freezing Equipment |
Refrigerators, freezers, cold storage, etc. |
|
Medical Equipment |
Ventilators, electrocardiographs, defibrillators, etc. |
|
Water pumps and sewage treatment systems |
Water pumps and sewage treatment systems |
|
Heating and air conditioning systems |
Heating and air conditioning systems |
|
Entertainment systems |
TVs, game consoles, audio systems, etc. |
Jackery Solar Generators for Emergencies
As a home emergency generator, a solar generator offers several key benefits: its quiet operation ensures minimal disruption during power outages, and its ability to provide clean, stable power protects sensitive electronics like medical devices and communication equipment.
Unlike traditional generators, it eliminates the need to store flammable fuels and the risk of carbon monoxide emissions, making it safer for indoor use. Its portability allows for easy relocation within the home to power essential appliances as needed.
Jackery is a well-known maker of high-quality solar products, including portable power stations, solar panels, and solar generators. Jackery Solar Generators have higher capabilities for powering home appliances for hours or days.
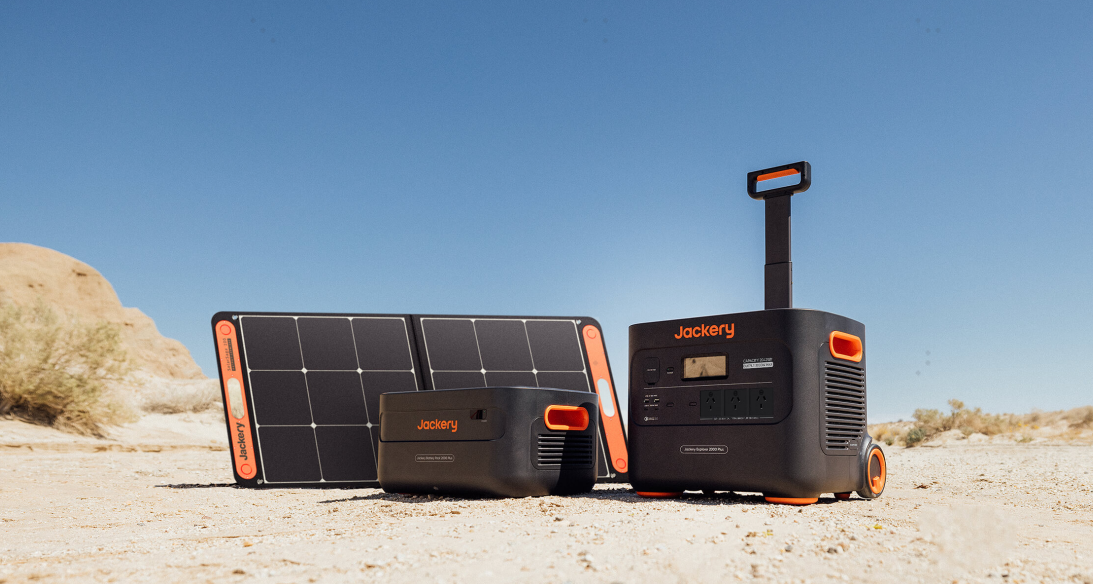
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus accommodates additional battery packs, enhancing its capacity from 2 kWh to an impressive 12 kWh, making it an ideal power solution for home emergency backup. The following are the components of a Jackery 2000 Plus.
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station
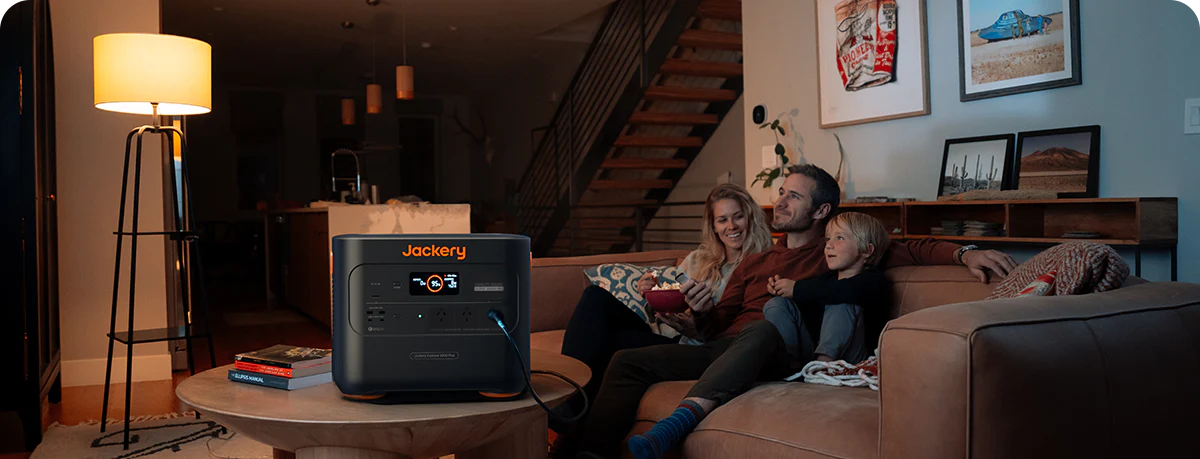
The Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station, with a capacity of 2042.8Wh, can support high-demand devices up to 3000W, including air conditioners, refrigerators, space heaters, etc., meeting the power requirements for residential applications. It operates at a sound level of 30 dB, comparable to a library, ensuring a tranquil environment.
Rapid wall charging achieves 100% in 1.7 hours, while solar charging requires 2 hours with six Jackery SolarSaga 200W panels. ChargeShield technology employs a distinct stepped variable-speed charging algorithm that improves safety and extends lifespan by 50%.
Monitor your power station's status in real-time through mobile devices, including metrics such as remaining battery level and output/input levels. Flexible connectivity options allow control of the power station via Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, enhancing its functionality in outdoor and indoor environments.
The LiFePO4 battery has a lifespan exceeding 10 years. Its capacity is maintained at 70% following 4000 charge cycles of daily use. Protections, including shock resistance and fire retardancy, ensure the solar generator's safety throughout its operation.
The Jackery SolarSaga 200W Solar Panel exhibits a solar conversion efficiency of up to 25%, facilitating rapid adoption of sustainable energy solutions. The ETFE-laminated case enhances durability, while the suggested angle maximises sunlight absorption, rendering it an ideal power source for outdoor excursions and home backup systems. It is portable and foldable and can be connected immediately to a power station for an optimal solar power system.

(*The working hours are only for reference; the actual working hours depend on your usage.)
How to Choose a Home Emergency Generator?
This section will examine the criteria for selecting the best emergency generator for your home.
Power Specifications and Load Capacity
Before acquiring an emergency generator, consider your power requirements. List the essential appliances and devices you'll need to power during an outage. Consider their wattage needs and compute the total power load. This will assist you in establishing the generator's minimum wattage capacity. A generator with a slightly higher wattage capacity is always recommended to be purchased to satisfy future power requirements.
Fuel Type and Availability
The most frequent fuel alternatives for emergency generators are petrol and diesel. Each fuel type has unique advantages and downsides. Petrol is commonly available and easy to store, but it has a short shelf life and may not be suitable for extended power outages. Diesel is efficient and widely available but requires frequent maintenance and may cost more upfront. Before deciding, consider each fuel's cost, availability, and storage requirements.
Noise Level and Environmental Impact
Generators can be noisy, especially if you live in a quiet neighbourhood or have nearby neighbours. Look for generators designed to work silently, such as "low noise" or "quiet run." Also, evaluate the generator's environmental impact. Look for vehicles that fulfil emission regulations and are eco-friendly.
Portability and Ease of Use
Determine whether you require a portable generator or a stationary standby generator. Portable generators are smaller, lighter, and easier to transport, making them ideal for occasional use. On the other hand, standby generators are more significant and permanently placed, providing automated power restoration during outages. When picking a generator, consider your demands and desired level of convenience.
In conclusion, many variables must be considered when selecting a generator. Based on the explanations above, we have a basic understanding of the home emergency generator; now, let us look at the benefits and drawbacks of various types of generators and their operating principles. Therefore, choose the most excellent home emergency generator for you.

Home Emergency Generators FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about the best emergency generators in Australia:
1. What size generator should I use for emergency power?
Finding the appropriate generator size is determined by the size of your home and your daily electricity requirements. Homes with numerous major electrical appliances, central air conditioning, and electric heat will want a more significant generator than those with fewer appliances and electrical requirements. However, most homes between 1,500 and 3,000 square feet require a generator rated between 17kW and 20kW.
2. Which kind of generator is the most efficient?
There is no clear solution to this. Diesel generators are often more efficient than gasoline or natural gas generators. However, more efficient generators are available, and diesel ones are unsuitable for all uses. Other efficiency concerns include the size of a structure and its power requirements. If your generator is overly firm, you may be using unnecessary fuel.
3. What kind of generator is ideal for household use?
A whole-house generator is the best way to power a home in most circumstances. A variety of factors can influence the best fuel source for you. For example, do you reside in a fire-prone area? If so, a gasoline generator may not be the best option. Remember, diesel is less flammable. Before purchasing a generator, continually analyse the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative.
4. Can I use a generator during severe weather?
While generators are designed to endure various situations, following manufacturer instructions is critical. Some generators have temperature or weather restrictions, so keep them within the prescribed range to ensure safety and peak performance.
Final Thoughts
With catastrophic weather and rising power grid instability in Australia, homes must be prepared for emergencies. A home emergency generator can provide peace of mind and prepare you and your family for unexpected events. Choosing the best emergency generator for your Australian house should not be taken lightly. Consider power requirements, fuel type, noise level, and portability to ensure you get a generator that matches your needs.