Specifics of Australia's National Energy Rebate Policy
Households
Australia's national energy bill rebate program financially relieves households struggling with high electricity costs. In 2024-2025, eligible households across most states will receive a $300 electricity rebate applied to their bills, broken into four quarterly credits of $75. To qualify, households must be recipients of government concession programs, including the Pensioner Concession Card, Veterans Affairs Gold Card, or low-income subsidies. The rebate is automatically applied to most consumers through their electricity providers.
However, the total savings for eligible households could vary according to their annual energy consumption and individual tariffs. Still, the rebate can provide modest relief on monthly bills. For households receiving income support, it can cut a percentage of their electricity costs. On top of this, specific state-level programs like the NSW Low Income Household Rebate can overlap for additional layers of electricity rebate relief. Financially, it could mean total annual savings of $385 in some states, which amplifies the relief for low-income or vulnerable consumers.
Embedded Network Households
Access to rebates might be complex due to different billing structures for households within embedded networks, including apartment complexes, caravan parks, and retirement communities. Unlike directly metered households, residents in embedded networks may face added barriers to receiving government rebates. Embedded networks are managed by an intermediary who buys electricity in bulk and resells it to the tenants. From September 2024, they can apply for the same $300 rebate as other households.[1] Nevertheless, they must go through a separate application process unless they qualify for one of the other electricity rebates like the NSW Family Energy or Low Income Household rebates. That's where they are automatically assessed for additional relief.
Network operators' administrative needs and involvement render rebate access less well-run for embedded network residents than households with direct retail accounts. Consequently, managing such rebate applications requires more effort, yet similar financial benefits are provided once they are in place. The same quarterly $75 credits reduce energy bills for eligible households.
Other Solar Subsidies in Australia
The Small Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES)
The Small Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) is a policy within Australia's Renewable Energy Target framework. It provides financial incentives through Small-scale Technology Certificates (STCs) for residential, commercial, and community groups installing solar photovoltaic systems, solar water heaters, air-source heat pumps, or other small-scale renewable systems under 100 kW.[2] The certificates echo the energy output of the system from the installation year up to 2030. Meanwhile, their number depends on the system size, location, and installation date.
The STCs are tradable and managed by installers or agents, so end-users can apply their value toward the upfront installation cost. Yet, STCs are calculated per each system's projected energy generation and vary by geographic zone. Systems in high-sunlight Queensland receive more certificates than those in lower-sunlight Tasmania. The value of the certificates fluctuates in the market for a dynamic pricing mechanism that installers monitor to offer pricing. While SRES helps cut upfront costs, customers must evaluate their zone and STC rebates to use the electricity rebate.
State-Level Solar Rebates and Incentives
Australia's states complement the SRES with their solar subsidy programs for local energy and economic goals. Victoria offers the Solar Homes Program for rebates of up to $2,225 for solar PV systems and interest-free loans for the same amount.[3] It is one of the state-level incentives. Further, Victorians can access up to $1,000 for solar hot water systems and are eligible for battery rebates. South Australia operates a separate Home Battery Scheme. It subsidizes battery storage for solar systems, so homeowners can store excess solar energy and use it during peak times.
Similarly, the Empowering Homes Program in New South Wales combines interest-free loans with solar installations for accessible transitions to renewable energy. Queensland and Western Australia offer feed-in tariffs, which are payments for excess solar energy to the grid. However, the value of such tariffs varies by region and can be adjusted based on regulatory changes. These state-level efforts and the national SRES lower financial obstacles to solar adoption in a multi-tiered manner. Still, eligibility and market dynamics must be acknowledged.
How to Lower a Household's Electricity Bill?
Replacing Older Appliances with Energy-Efficient Models
Upgrading contemporary, energy-efficient appliances with government electricity rebate programs can yield electricity savings. Older appliances may use inefficient technology and consume more power than necessary. E.g., replacing a traditional air conditioner with a new inverter model can cut energy consumption. Newer appliances have variable-speed compressors and temperature controls to use energy only when needed. It lowers the strain on the grid during peak times to further drive down electricity consumption. Also, some models integrate with home energy management systems to optimize energy usage per real-time electricity prices or grid demand.
When utilizing an electricity rebate, the cost of these upgrades is lowered. The appliance replacement schemes in New South Wales provide rebates that cover 40-50% of the cost. It helps families replace fridges and washing machines with energy-efficient alternatives. The schemes enable some families to access appliances that might otherwise be financially out of reach. It allows them to save $325 annually on power bills while contributing to long-term carbon. [4]
Using LED Lights
Switching from incandescent to LED lighting is a low-hanging fruit in energy efficiency. LEDs consume 75% less energy than incandescent lighting and can last 25 times longer.[5] Thanks to LEDs, most of their energy is converted into light rather than heat. For homes, it implies that LEDs lower electricity bills and cooling needs in warmer climates with less ambient heat. Plus, many LED systems today are compatible with smart home setups for dimmable options and customizable color temperatures. It can also optimize energy use throughout the day.
Electricity rebates targeting lighting upgrades can render this change more attractive. Many state schemes, including the Energy Savings Scheme in NSW, offer rebates for households that install LED lights through accredited suppliers. It benefits large homes; lighting accounts for a portion of the energy bill. With smart lighting systems, the savings become even greater. The reason is that such systems can operate only when needed, which helps decrease energy expenditures.
Utilizing Timers and Smart Home Devices
Smart home devices and timers in household systems can adjust energy use with less waste during non-peak hours. For instance, smart thermostats can adjust heating and cooling systems according to occupancy, weather patterns, and personal preferences, so energy is used only when necessary. Similarly, smart plugs can power down televisions and computers when not in use. With energy data collected over time, the devices can also suggest optimizations to lower consumption.
Rebate programs may extend to smart home technology for households modernizing their energy systems. Victoria's Energy Upgrades Program supports installing smart devices that can automate turning off lighting or adjusting HVAC(Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems during peak electricity pricing. The combined savings can bring noticeable diminutions in energy usage and costs.
Solar Generators
Installing solar generators with battery systems can be a game-changer for households slashing their electricity bills. They capture sunlight and store energy during peak demand periods when electricity prices are higher. Solar systems also have smart inverters that can interface with a home's energy management system to distribute power. While stockpiling energy during off-peak hours and using it later, households can curtail reliance on the grid and their energy bills.
With the electricity rebate NSW Rebate Swap initiative, households can trade future rebate savings for solar fittings. It lets eligible homes install solar systems and use years of electricity discount savings upfront. So, it lessens the initial installation's financial burden and locks in energy savings for the next decade. Further, solar systems connected to the grid via APPs can provide financial incentives. Households are reimbursed for contributing stored energy during peak demand.
Our Recommendations: Jackery Solar Generators
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus

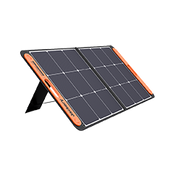
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is a power solution for Australian families pursuing an electricity rebate and to lower their electricity bills. It has a 2042Wh capacity and offers a 3000W output, which can power heavy-duty household refrigerators (up to 2200W for 2.3 hours), electric ovens (800W for 2.1 hours), and induction cookers (2100W for 0.7 hours). It functions during power outages or off-grid scenarios with a capacity that reaches up to 12kWh. Depending on your setup, you can run a home independently for up to one week. We've made it with a LiFePO4 battery with a 10-year life and over 4000 charge cycles for stable performance.
You can charge it in 1.7 hours using AC or 6 hours with solar with six Jackery SolarSaga 100W Solar Panels. It confirms that the generator can be recharged during sunny days while off the grid. The 20ms switch time of its EPS keeps CPAP machines and refrigerators powered during outages for the lower strain on local grid systems. Its 25% solar conversion efficiency exploits power capture in low-light conditions for rural areas with partial sun exposure. The quiet operation at 30dB guarantees that it fits into residential settings. Pairing the generator with an electricity rebate program is economical. It lets families use government incentives while cutting down their utility bills.
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Capacity |
2042Wh |
|
Output |
3000W |
|
Household Usage |
Refrigerators (up to 2200W for 2.3 hours), Electric ovens (800W for 2.1 hours), Induction cookers (2100W for 0.7 hours) |
|
Off-Grid Capability |
Can run a home independently for up to one week |
|
Battery Type |
LiFePO4 with a 10-year life and over 4000 charge cycles |
|
Recharge Time |
AC: 1.7 hours, Solar (six Jackery SolarSaga 100W Solar Panels): 6 hours |
|
EPS Switch Time |
20ms for uninterrupted power during outages |
|
Solar Conversion Efficiency |
25% |
|
Operation Noise |
30dB for quiet residential use |
Jackery Solar Generator 600 Plus

The Jackery Solar Generator 600 Plus is dense yet capable of maximizing its electricity rebate benefits. With a 632Wh capacity and an 800W output, it powers mobile phones (29W, charged 27 times), laptops (80W, charged seven times), and camping lights (3W, lasting 54 hours). It's lightweight at 7.3 kg for outdoor and indoor use. Its portable power station has a LiFePO4 battery with 4000 charge cycles at 70%+ efficiency, so users won't replace the unit for years.
For faster charging, you can recharge it via wall outlets in 1.6 hours or solar charging (two Jackery SolarSaga 100W Solar Panels) in 4.3 hours. An electricity rebate makes it more attractive for families to decrease their reliance on the grid for power during outages or living off the grid. Its UPS functionality with a <20ms switch time ensures desktop computers and refrigerators run without interruption to avoid data loss or spoilage. It also has ChargeShield 2.0 technology for better charging safety and battery life by 30% through variable-speed charging. Also, the whisper-quiet operation at ≤22dB suits indoor situations without noise disturbances. The compact generator helps households use solar power rebates to become energy-independent with agility, trustworthiness, and energy economy.
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Capacity |
632Wh |
|
Output |
800W |
|
Device Charging |
Mobile phones (29W, 27 times), Laptops (80W, 7 times), Camping lights (3W, 54 hours) |
|
Weight |
7.3 kg (suitable for indoor and outdoor use) |
|
Battery Type |
LiFePO4 with 4000 charge cycles at 70%+ efficiency |
|
Recharge Time |
Wall outlet: 1.6 hours, Solar charging (two 100W panels): 4.3 hours |
|
Electricity Rebate |
Helps families reduce grid reliance and decrease bills |
|
UPS Functionality |
<20ms switch time for uninterrupted power supply |
|
ChargeShield 2.0 |
Improves charging safety and extends battery life by 30% |
|
Operation Noise |
≤22dB (whisper-quiet for indoor use) |
Conclusion
Energy rebates offer financial relief for Australian families coping with high energy costs while cutting the upfront investment for energy-efficient upgrades, solar panels, heat pumps, or home insulation. Electricity rebates help households lower their consumption and reliance on grid-supplied electricity by incentivizing renewable technologies to reduce energy bills over time. Additionally, they moderate the financial impact of moving from older, less efficient appliances to more energy-efficient options. Likewise, the rebates help families manage rising electricity costs during peak demand seasons with off-peak consumption and energy storage solutions.
Rebates also increase access to clean energy for lower-income households, where upfront costs are a barrier. It nurtures greater equity in energy accessibility. Also, they stimulate broader societal benefits with lower demand on the energy grid, which avoids blackouts and carbon emissions to back national sustainability goals. Rebates can promote local job creation in renewable energy sectors. Increased demand for energy-efficient solutions stimulates economic activity. Last but not least, energy rebates may encourage families to consider long-term financial planning for energy usage. It allows them to discover the perks of a decentralized energy supply through intelligent thermostats or grid-connected solar systems for a resilient, future-proof home energy strategy.
Reference:
[1] https://www.service.nsw.gov.au/transaction/household-national-energy-bill-relief
[2] https://www.solarchoice.net.au/learn/solar-rebates/solar-credits-and-rebates/
[3] https://www.solarchoice.net.au/learn/solar-rebates/state/victoria/
[4] https://www.nsw.gov.au/news/appliance-replacement-scheme-slashes-power-bills