|
Key Takeaways: |
|
• Wattage law is a fundamental principle of electrical engineering that describes the relationship between different parameters such as voltage (V), current (I), and power (P) in an electrical circuit. • Watt's Law Triangle is a convenient visualisation tool. • Watt's Law and Ohm's Law are two basic principles discussing current circuit behaviour. • The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus has 632Wh (15.2Ah/41.6V DC) capacity and Explorer 300 Plus has 288Wh (12.8V/22.5Ah) capacity. • Understanding Watt's Law is essential for those who want to optimise and maintain solar energy systems. |
What Is Wattage Law?
Watt's Law is named after James Watt, a Scottish engineer known for his improvements to the steam engine in the late 18th century. While he may not have worked directly in electrical engineering, his innovations in steam engine technology significantly impacted various fields, including electrical engineering.
Definition of Watt's Law
Wattage Law is a fundamental principle of electrical engineering that describes the relationship between different parameters such as voltage (V), current (I), and power (P) in an electrical circuit.
In simple terms, voltage (V) is the electrical push, current (I) is the flow of electricity, and power (P) is how fast the energy moves. Here's an introduction to the different parameters of Watt's Law:
Voltage (V)
Voltage (V) is the difference of potential between two points in a circuit. Any potential difference causes electrons to flow from a higher potential point to a lower potential point, thus generating electricity. Volts are the units of voltage (V).
Current (I)
Current (I) is the amount of electricity flowing through a circuit at any given time. Its unit is amperes or "amps" (A). Current can only flow when there is a potential difference.
Power (P)
Power (P) measures the work a circuit or component can do per unit of time. Simply, it is the amount of electrical energy transferred per unit of time. The power unit is joules per second (J/sec), also known as watts (W).
How to Understand the Relationship between Voltage (V), Current (I) and Power (P)?
To better understand Watt's Law, you must understand the relationship between different parameters. Let's use an everyday example to explain the relationship between voltage (V), current (I) and power (P):
Suppose a light bulb is connected to a circuit. The electric potential (voltage) pushes the charge through the light bulb's filament, creating a flow of electrons (current). When the electrons flow, they generate heat and light, the light bulb's energy output (power). Finally, the wattage of the light bulb represents the energy consumed per second.
Wattage Law Formula and Examples
The formula of Watt's Law shows the relationship between power (watts), current (amperes), and voltage (volts). The formula of Watt's Law is as follows:
Power=Voltage*Current (P=V*I)
Voltage=Power/Current (V=P/I)
Current=Power/Voltage (I = P/V)
The following content presents some examples to better explain the formula of Watt's Law better.
Example 1 of Watt's Law Formula
What is the current if the bulb's voltage is 120 volts and the power is 30 watts?
• First, the voltage and power of the bulb are 120V and 30W, respectively.
• Just substitute the corresponding data into I = P/V to calculate.
I = 30/120
I=0.25A
Example 2 of Watt's Law Formula
How do you calculate the current consumed by common bulbs in life?
• Take a common 100-watt bulb as an example. The voltage of the bulb is usually 110V or 220V.
• Just substitute the corresponding data into I = P/V to calculate.
I = 100W / 110V
I = 0.91A
I = 100W / 220V
I = 0.45A
So, a 100-watt bulb at 110V draws about 0.91 amps, and a 100-watt bulb at 220V draws about 0.45 amps.
Example 3 of Watt's Law Formula
Suppose you want to know how many 300-watt lighting fixtures you can plug into a circuit without blowing a fuse.
• First, you need to know that most homes have a 15-amp circuit. Most circuit breakers have a 20-amp circuit.
• Simply plug that into P = V * I to calculate.
P = 110 * 20
P = 2200W
So, any appliance or electronic device plugged into the circuit must be less than 2200 watts because 2200 watts is all the power available on that circuit. Finally, you can safely plug seven 300-watt lamps into the circuit, with a 100-watt safety margin.
Watt's Law Triangle
Watt’s Law Triangle is a handy visual tool for quickly solving circuit problems involving voltage, current, and power.

Each side of Watt's Law Triangle represents a variable, and its formula is found by covering the required variable and solving for the remaining two variables. It makes Watt's Law Triangle particularly useful when working with complex circuits or when quick calculations are needed.
Here are three formulas that can be intuitively derived from Watt's Law Triangle:
To find power (P), multiply current (I) by voltage (V).
P = I * V
To find voltage (V), divide power (P) by current (I).
V = P / I
To find the current (I), divide power (P) by voltage (V).
I = P / V
The electrical power in a circuit can be calculated using the three formulas in the above Watt's Law Triangle. If the calculated power is positive, the device consumes or uses power. But if the calculated power is negative, the component generates or generates power.
Watt's Law VS Ohm's Law
Watt's and Ohm's laws are fundamental principles that discuss current circuit behaviour. They are related and can be used to solve different circuit problems.
Watt's Law defines the relationship between a circuit's volts and current power.
Ohm's Law explains and defines the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
According to Ohm's Law, current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance.
The formula for Ohm's Law is:
V = I * R
I = V / R
R = V / I
In the formula, I is current, R is resistance, and V is voltage.
The figure below is the Ohm Law Pie Chart that clearly shows the parameters of Ohm's Law.

If Ohm's Law is substituted into Watt's Law, a new formula is obtained:
P = V^2 / R or P = I^2 x R
The above formula explains that the power used by an electrical device is proportional to the voltage applied to the square and inversely proportional to the circuit resistance.
To more clearly distinguish between Watt's Law and Ohm's Law, the following table is listed for reference:
|
|
Watt's Law |
Ohm's Law |
|
Definition |
It measures the power consumption in a circuit. |
It finds the current and resistance values in a circuit. |
|
Formula |
P = V * I V = P / I I = P / V |
V = I * R I = V / R R = V / I |
|
Practical Application |
It is applied to calculate the electrical components in a circuit. |
It is used to determine the resistance of a circuit. |
Applications of Wattage Law
Whether you are determining an appliance's power consumption or determining a conductor's size for a specific load, Watt's Law remains constant.
By understanding and applying this fundamental principle, more professionals in related fields can continue to innovate, improve energy efficiency, and reduce environmental impact. Therefore, Watt's Law has many uses and applies to different scenarios. Some practical applications of Watt's Law include:
Determining Energy Consumption
One of the most practical applications of Watt's Law is determining energy consumption. By knowing the voltage and current values of a specific device, Watt's Law can calculate the power consumed by the device. The information calculated by Watt's Law can be used to manage energy use in homes, businesses, and industrial environments.
Improving Energy Efficiency
Watt's Law is also critical when managing data centres and server farms. Because energy efficiency is the most crucial factor in these related fields, most related fields can furthest reduce operating costs and minimise environmental impact by optimising the power usage of facilities. Electrical engineers often use the principles of Watt's Law to ensure that the power distribution system in related facilities is designed for maximum efficiency, providing reliable service without consuming excessive energy.
Understanding Electrical Engineering Principles
Electrical engineers and technicians must apply Watt's Law to electrical circuits. Electrical engineers use Watt's Law to analyse the performance of electrical components, troubleshoot circuit problems, and ensure that equipment operates at optimal conditions. In addition, Watt's Law can be used to design and maintain transmission lines to ensure that electricity is distributed efficiently to homes and businesses.
Watt's Law has contributed significantly to understanding electrical engineering principles and has many practical applications. In addition, Watt's Law is the fundamental principle for designing and maintaining efficient electrical systems.
Laying the Foundation for Professional Education
In an educational setting, Watt's Law is a fundamental concept for teaching the basics of electromagnetism. A solid understanding of Watt's Law lays the foundation for mastering more advanced concepts in electrical engineering. Therefore, students studying physics, electrical engineering, or related fields will inevitably encounter Watt's Law during their studies.
Promoting the Development of Renewable Energy
Watt's Law has many practical applications in today's world. Developing renewable energy systems such as solar and wind turbines is essential for optimising power output and consumption.
Engineers rely on Watt's Law to design efficient battery systems and charging stations for electric vehicles, providing optimal power delivery to electric cars. In addition, Watt's Law determines the charging current required for a specific battery capacity and charging time, ensuring a seamless and convenient electric vehicle charging experience for users.
Promoting the Development of the Electronics Industry
By understanding Watt's Law, manufacturers can design electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and TVs that consume less energy while maintaining high performance. The energy efficiency brought about by Watt's Law contributes to reducing their environmental impact and providing long-term consumer benefits.
Watt's Law and Solar Energy Systems
Watt's Law is essential to understanding and using solar energy in your home. Watt's Law helps you measure how much electricity your solar panels can generate. It lets you determine the appropriate number of panels, the best installation location, and your home's energy needs. Therefore, understanding Watt's Law is essential for optimising and maintaining their solar energy system.

Amperes in Solar Systems
In solar systems, the flow of electrical current is measured in amperes. Amperes are produced when electrons from silicon atoms are freed from sunlight photons.
The value of an ampere depends on the following factors:
• Solar panel size
• Sunlight intensity
• Characteristics of the connected circuit
The importance of amperes in solar systems is as follows:
• Amperes help in power calculations, as power is calculated by multiplying amperes by voltage.
• The exact value of amperes is essential in designing a solar power system.
• Calculating amperes from watts and voltage helps determine the battery capacity in amp-hours.
Watts in Solar Systems
The rate of solar systems at which energy is consumed and generated is calculated in watts.
The critical importance of Watts in Solar Systems is as follows:
• Watts helps determine the configuration and size of solar panels or solar generators required.
• The cost of solar panels can also be determined by wattage; the higher the wattage, the higher the cost.
• Higher wattage solar panels take up less space. So, high-wattage panels are essential for areas with less space.
• High-wattage solar panels are the best choice when the intensity of sunlight is low.
Volts in Solar Energy
The force that moves the current through a circuit is called voltage. In solar energy systems, the electrical potential generated is also called voltage.
The importance of Volts in Solar Energy Systems is as follows:
• Volts ensure compatibility between solar energy components like solar cells and inverters.
• The series or parallel arrangement of solar panels can also be defined by voltage.
• Voltage affects the efficiency of solar panels as it depends on shading, temperature, age of panels, etc.
Practical Application of Amps, Watts and Volts in Solar Systems
How do Amps, Watts and Volts relate to solar panel installations? Solar systems' design, function and efficiency depend on the basic principles of Amps, Watts and Volts.
Amps
The current in solar panels flows from the panels to the inverter and finally to the battery. Amps help select installation equipment such as circuit breakers, fuses, and wires. The charging and discharging of batteries also depend on amperes.
Watts
Watts help determine the size of a solar system, which means knowing the number of solar panels required. Watts can evaluate the return on investment and performance evaluation of solar installations.
Volts
The efficiency of a solar system and the compatibility of solar components can be determined by voltage.
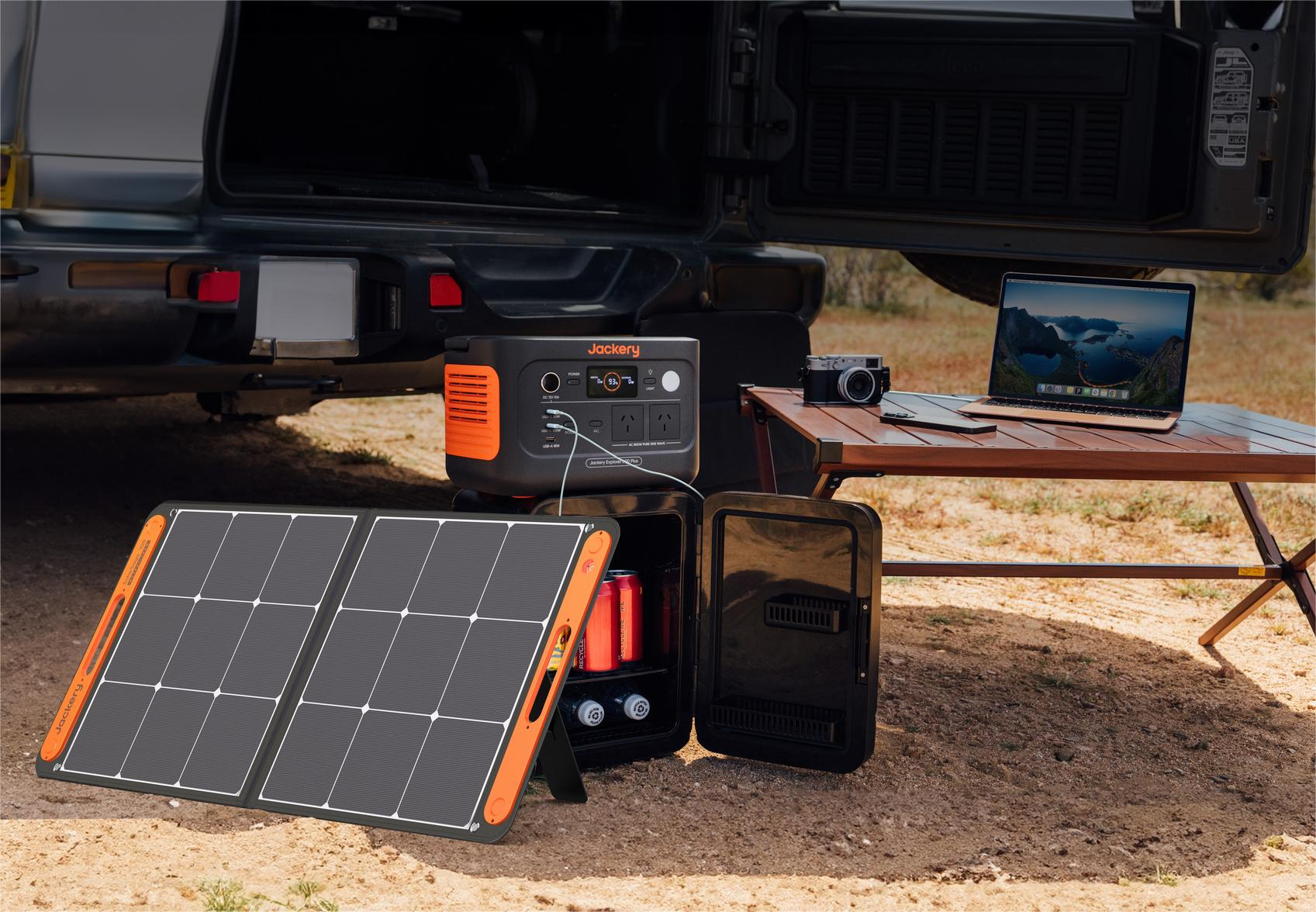
Jackery Portable Power Stations Explained
A key idea in electrical systems is the power formula, sometimes referred to as the wattage law: Voltage (volts) × Current (amperes) equals Power (watts). Understanding this regulation is essential when selecting a power source for your house or outdoor activities.

Jackery Portable Power Stations offer a stable power source that can effectively charge household or outdoor appliances. When used with Jackery Solar Panels, they maximise solar energy capture and storage, guaranteeing you will always have electricity available.
It makes this computation easier and guarantees that you have the appropriate wattage for your requirements. Whether powering appliances during a blackout or setting up a small camp, Jackery guarantees effective and convenient energy management. Jackery Portable Power Station also offers various charging choices, such as solar panels, carports, wall outlets, and other electric sources, to provide a versatile and reliable energy source.
Jackery Explorer 600 Plus
The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus is the ideal portable power option. With its 800W output and 632Wh capacity, it can power many outdoor devices, from coolers to camping lights. The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus is your go-to power station for all your activities because it is strong, durable, and light. It makes charging fun things to do outside easy.
Our improved technology lets you charge more efficiently than ever. You can quickly charge your gadgets and use them for longer. No matter where you go, stay charged and linked. Charges that are reliable and work well, customised to your needs.
The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus is the best compact power station for all outdoor activities. It's intended to be as convenient as possible and easy to store, weighing only 7.3 kg (16.1 lbs) and very small. The handle folds up, making it easy to take with you. You can always get power to stay connected and charged no matter where your travels take you.

Working Hours of Jackery Explorer 600 Plus:
Projector (100W): 5H
Coffee Maker (550W): 1H
Portable Cooler (60W): 6H
Laptop (80W): 7 Times
Camera (8.4W): 27 Times
|
*Review from Our User |
|
I bought the Jackery Explorer 600 plus to serve as the power source for my electric guitar busking. I had my first busking session last Friday, and the unit performed excellently. It efficiently powers my large speaker, mixer, and guitar effects unit, using only 11% in an hour and a half while running all that equipment. |
Jackery Explorer 300 Plus
It introduces the Jackery Explorer 300 Plus Portable Power Station, a small, cutting-edge gadget for fueling daily excursions. The 300 Plus offers a dependable, portable, multipurpose energy source thanks to its sturdy construction and lightweight design. At just 3.75 kg, it is the ideal hiking, camping, or disaster preparedness partner because it fits easily into your bag.
With its 288Wh capacity and 300W output, this portable power station can charge various gadgets, including laptops, smartphones, and small appliances. Thanks to the dual USB-C ports' 100W fast-charging capacity, multiple devices can be charged simultaneously. Its flexibility shines with four charging methods: harness solar energy, plug it into a wall outlet, use a carport, or charge via USB-C. You'll have access to convenient, efficient power no matter where you are.
The Explorer 300 Plus is more than just a power station—it's a sustainable energy solution. Its whisper-quiet operation and zero emissions make it eco-friendly and ideal for off-grid living. Its durable LFP battery ensures a lifespan of 10 years with over 3,000 cycles to 80% capacity, setting a high standard for longevity and reliability.
The 300 Plus features advanced ChargeShield Technology, designed with safety in mind. It protects you and your devices from potential risks. Experience unparalleled convenience and performance with this all-in-one portable power station.

Working Hours of Jackery Explorer 300 Plus:
Laptop (80W): 2.2 Times
Smartphone (29W): 13 Times
Camera (8.4W): 12 Times
Portable Speaker (10W): 18H
Drone (90W): 5 Times
|
*Review from Our User |
|
The units are well-constructed, lightweight, and highly dependable. I have several exciting ideas for this unit, including camping, road trips, and backup equipment. This unit is highly recommended, and I intend to purchase additional ones and backups that offer greater capacity. |
Wattage Law FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about the wattage law.
1. What are some practical applications of Watt's Law formula in daily life?
Here are some practical applications of Watt's Law formula:
• Watt's Law formula can be used to measure the power requirements of individual components.
• Watt's Law formula can help homeowners safely add new appliances or electrical equipment to their homes, ensuring the circuits are not overloaded.
• Watt's Law formula can be used to calculate the power of new electrical equipment in buildings, factories, stores, etc.
• Watt's Law formula can be used to determine the appropriate wire size for a building.
2. What are the benefits of Watt's Law for homeowners?
Overall, homeowners can use Watt's Law to make intelligent choices, conserve energy, and keep their homes safe. Watt's Law can help homeowners lower their monthly electricity bills by allowing them to choose energy-efficient appliances and use electricity wisely.
• Homeowners can use Watt's Law to calculate home appliances' power consumption, understand a circuit's electrical load, and determine the appropriate size of electrical components for home improvement projects.
• Homeowners can also use Watt's Law to prevent circuit overloads and ensure electrical safety.
• Watt's Law can help homeowners safely add new appliances or electrical equipment.
3. What are some common misconceptions about amps, watts, and volts in solar systems?
Amps, watts, and volts can be used to select the right solar system, but some common misconceptions can also occur. Some common misconceptions are listed below:
• The higher the amperage, the more influential the solar system. The power of a solar system depends on both voltage and amperage. So, increasing the amperage of a solar system alone does not increase its power.
• Higher voltage always makes a solar system more efficient. At the correct value for a solar system, voltage increases efficiency and reduces current. However, using very high voltages can damage components in a solar system.
Final Thoughts
In summary, although Wattage Law is not a panacea, electrical engineers can use it to ensure that electrical systems operate securely and efficiently. Understanding the basics of Wattage Law allows most homeowners to make wise decisions about electricity use. This guide details Watt's Law's definition, formula, application, and related concepts. I hope it will give you a deeper understanding of Watt's Law.