Ultimate Guide to Amps, Watts, and Volts With Jackery
Ultimate Guide to Amps, Watts, and Volts With Jackery
Electricity has become a crucial part of our day-to-day life, and imagining living without power seems impossible. As solar energy is a safe, renewable, and clean alternative for homes, many people are investing in solar power stations.
However, it's worth noting the power station's amps, watts, voltage, etc., to ensure it can power appliances for long hours. Jackery Explorer Portable Power Stations are large-capacity solar solutions with high watts, volts, and amps values.

In this guide, we will take a deep dive into electrical terms. We will focus on calculating voltage, watts, amps, etc., and on choosing the ideal-sized power station.
What Are Amps, Watts, And Volts?
When understanding the nitty-gritty of electricity, it's crucial to learn basic electronic terms like amps, watts, voltage, and ohm.
Identifying the watt, ampere, voltage, and ohms for any power station is vital to confirming compatibility with your home or outdoor appliances. On the contrary, powering equipment using a wrong voltage battery is the primary reason for appliance operation failure.
The best part about these basic electrical terms is that they are interrelated and can be calculated using a simple formula. For example, you can calculate the watts an appliance consumes by multiplying amps and volts. Let us discuss how amps, watts, voltage, and ohms differ.
Why Convert Watts to Amps?
Amperes, commonly called amps, measure the number of electrons flowing through a certain point per second. In other words, it describes the current flow through an electrical circuit.
In mathematical terms, amps are equal to watts divided by volts of a specific appliance.
Formula: Amps = Watts / Volts
If you have the watts and volts of an appliance, you can easily calculate its amps. For example, if the watts and volts of an electric device are 3600W and 240V, respectively, the amps value will be:
Amps = 3600W / 240V = 15A.
Amperage is the strength of the electric current and is expressed in amperes. The larger the amperage, the more electricity can flow through the circuit.
What Is A Watt?
Wattage, commonly known as watts, is the power an electric appliance consumes. In other words, it is defined as the "electricity at work" or power a device takes to run.
In mathematical terms, watts are equal to the multiplication of amps and volts.
Formula: Watts = Amps × Volts
For instance, if an electric device uses 10 amps and 240 volts, the wattage will be:
Watts = 10 amps × 240 volts = 2400W.
The higher the wattage, the more the output and power of the appliance.
What Is A Volt?
Volt measures the force or pressure required for an electric current to flow past a wire. In other words, it also determines the speed at which individual electrons flow through the circuit.
Large home appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners operate at 240V. On the contrary, smaller devices like computers, TVs, light bulbs, etc., operate at 120V.
In mathematical terms, volts are equal to the watts of an appliance divided by its amps.
Formula: Volts = Watts / Amps
If the appliance consumes 500 watts and 25 amps, the volts can be calculated as:
Volts = 500W / 25A = 20V
What Is An Ohm?
The resistance inherent in an electric wire encountered by the electrons while flowing from high to low is called ohm.
In other words, it is the electrical resistance between two points of a conductor. When one volt of constant potential difference is applied to these points and produces a current of one ampere, the natural resistance equals one ohm.
Formula: Ohm = Volts / Amps
Or, Ω = V / A
For example, if there is 240V and 12A, the natural resistance of the conductor will be:
Ω = 240V / 12A = 20 Ω
Amps, Watts, And Volts Relations
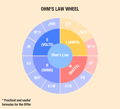
Amps, Watts, And Volts Formulas
Understand Amps, Watts, And Volts In the Electrical System
The Electrical Efficiency
Jackery Power Stations Explained

Capacity
Recharging Time
Ports
Appliances
2160Wh (43.2V/50Ah)
Explorer 2000 Pro + 6*SolarSaga 100W: 5.5H
AC Adapter: 2H
12V Car Adapter: 24H
2*AC Output: 230V, 2200W (peak 4400W); 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0x2, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 15V, 12V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A
TV(200W): 8.4H
Refrigerator(700W): 2.4H
Microwave(750W): 2.2H
Coffee Maker(800W): 2.1H
Blender(300W): 5.6H
Stove(850W): 2H

Capacity
Recharging Time
Ports
Appliances
1002Wh (43.2V, 23.2Ah)
Explorer 1000 Pro + 6*SolarSaga 80W: 9H
AC Adapter: 1.8H
12V Car Adapter: 12H
2*AC Output: 230V, 1000W, peak 2000W; 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0x2, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 15V, 12V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A
TV(200W): 4H
Fridge(500W): 1.6H
Blender(300W): 2.7H
CPAP Machine(100W): 8H
Computer(200W): 4H
Electric Wheelchair(380W): 2.1H

Capacity
Recharging Time
Ports
Appliances
518Wh (21.6V, 24Ah)
Explorer 500 + 1*SolarSaga 100W: 9.5H
AC Adapter: 7.5H
12V Car Adapter: 7.5H
1*AC Output: 240V, 500W (peak 1000W); 2*DC Output: 12V⎓7A; 3*USB-A: 5V⎓2.4A; 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A
Phone(10W): 44H
TV(60W): 7.3H
Fan(100W): 4.4H
Lighting(25W): 17.6H
Speaker(120W): 3.7H
Computer(200W): 2.2H
Amps, Watts, And Volts FAQs
1. How many amps are in 10 watts at 120 volts?
You can calculate the amps by dividing the given watts by volts.
Amps = Watts ÷ Volts = 10W ÷ 120V = 0.083A
Here we have a few more ampere calculations with different power and volts.
Power (W)
Voltage (V)
Current (A)
10 Watts
120 Volts
0.0833 amps
20 Watts
120 Volts
0.167 amps
30 Watts
120 Volts
0.250 amps
40 Watts
120 Volts
0.333 amps
50 Watts
120 Volts
0.417 amps
60 Watts
120 Volts
0.500 amps
70 Watts
120 Volts
0.583 amps
2. Does higher watts mean more power?
In short, yes. As watts represent the rate at which energy is used or transferred, it is directly related to power. The higher the watts of a battery capacity, the more power.
3. What are the differences between amps, watts, and volts? Is watts stronger than volts?
Here is a brief definition of wattage, amps, volts, etc.
Amps measure the electrical current or the speed at which electrons flow through a conductor.
Volts measure the electrical voltage and represent the difference in electrical potential.
Watts is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred in a circuit.
Watts measure power, while volts represent electrical potential. That being said, the energy used or transferred is calculated in watts. Therefore, watts are stronger than volts.
Final Thoughts
Knowing the current flowing the load is vital in choosing the best wire. The amps, watts, voltage, and ohms formulas are also helpful in calculating the size of the solar inverter and total power consumption. Once you know how much power your appliances consume, you can easily calculate the portable power station size.
Depending on your power needs, you can choose Jackery Explorer Portable Power Stations, available in different sizes. If you want to power all small and large home or outdoor appliances for hours, consider investing in the ultimate power solution Jackery Explorer 2000 Pro Portable Power Station.
PAGE CONTENTS
New Arrival
Hurry up! Sale ends once the timer hits zero