|
Key Takeaways: |
|
• A solar farm is a large-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) system designed to supply commercial electricity to the grid. • A solar farm uses photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity. • Australia has several types of solar farms, each with its purpose. • Solar farms benefit the environment while also promoting agriculture and solar technology. • We highly recommend Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus or 1000 Plus to charge your household appliances with solar energy. • Many variables affect the construction of a solar farm in Australia. Starting a solar farm in Australia is a complex and capital-intensive process. |
What Is a Solar Farm?
A solar farm is a large-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) system that supplies commercial electricity to the grid. It is much larger than residential ones and can cover acres of land. A solar farm can also be called a solar field, solar park, photovoltaic power station, large-scale solar power (LSS), or solar power plant. Solar farms use sunlight and convert it into electricity through thousands of solar panels arranged in a field or desert area.
Solar farms are primarily built in rural Australia because they require a lot of space to accommodate the rows of photovoltaic (PV) solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity.
Solar farms are designed to produce solar energy on a large scale and usually consist of multiple rows of parallel solar panels. Solar farms produce large amounts of solar energy and deliver it directly to the grid connection system, unlike the small solar panels that are usually used to power a single home or building.
A photovoltaic power station is a collection of large numbers of solar panels (photovoltaic cells) in a community, which are installed on the ground or rooftops. Photovoltaic cells produce clean, green solar energy that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions. The electricity is then delivered to nearby homes and businesses.
How Does a Solar Farm Work?
Solar farms work by converting sunlight into electricity using solar panels. Unlike rooftop panels that power individual homes or units, solar farms produce energy on a large scale, fed into a grid for distribution to homes and businesses.

Harvesting the Sun: One of the main components of a solar farm is the solar photovoltaic panel. These panels contain solar cells made of silicon layers or other materials that can generate an electric field. The number and type of solar panels used in a solar farm depends on the size and location of the farm. When the sun hits the photovoltaic panel, it excites the electrons in the solar cells, producing direct current (DC).
Inverter Conversion: Another essential part of a solar farm is the inverter. An inverter converts DC power generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with the grid and can be used in homes, businesses and industries. Various inverters are available, including string, microinverters, and power optimisers.
Integration with the Grid: The converted AC electricity is integrated into the local grid to be distributed to homes and businesses. The figure below is a schematic diagram of how solar farms work.
What Are the Benefits of Solar Farms?
Solar energy can be an efficient alternative to fossil fuels. Some of the many benefits of solar farms include:
Benefits for the Environment
Solar energy has unique environmental advantages because it does not emit waste products like carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, or nitrogen oxides linked to respiratory problems. , acid rain and global warming. Studies have shown that one acre of solar panels can offset more carbon emissions per year than one acre of carbon-sequestering trees.
Also, sunlight is an inexhaustible natural resource that can be used continuously. The abundant sunlight in most parts of the world makes solar power plants an ideal source of electricity generation in many areas.
Create a Large Number of Jobs
Solar farms help create jobs at all stages. The development phase requires engineering and project management professionals and the construction phase requires skilled and unskilled labour.
There are also many jobs in the production and transportation of solar panels. Increased commercial activity during construction benefits the local economy. The installation and maintenance of solar farms also create many jobs in related industries.
Boosting Agriculture
Using solar farms to power irrigation systems can improve farm water management. Irrigation is essential to agriculture, but traditional methods of using electricity or fuel to drive pumps often wastewater and increase costs. By turning to solar farms for power irrigation, farmers can reduce their energy bills and adopt more sustainable and cost-effective methods, ultimately reducing their carbon footprint.
Boosting Solar Technology
As solar farms become more popular, scientists and engineers continue to develop solar panel technologies that are more efficient, effective, and less toxic. More mature solar technology can make solar panels cheaper and more accessible for companies and ordinary consumers.
Saving Electricity Costs
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the cost of electricity has continued to rise over the past few decades, increasing by 60% in the past decade alone.
A farm's electrical needs, including water systems, machinery, and lighting, incur huge costs. These high electricity costs are a burden on farmers. Solar farms allow farmers to reduce their dependence on electricity and bring long-term cost savings.
Types of Solar Farms in Australia
Solar farms are a wise investment considering the low maintenance costs, low energy bills and profitable income. There are several types of solar farms in Australia, each with its own purpose. They have the potential to boost local economies while reducing the effects of climate change by reducing emissions and providing renewable energy.

Common Solar Farm Types in Australia
Solar farms are divided into two main categories based on their size: utility-scale solar farms and community solar farms.
1. Utility-Scale Solar Farms
Utility-scale solar farms cover a wide area, are large in scale, connected to the grid, and power thousands or tens of thousands of homes and businesses. It can produce more than 10 megawatts of electricity, which is used to supply electricity to local utilities.
To give you an idea of how much electricity a utility-scale solar farm can generate, 1 megawatt can power 200 homes. These huge solar farms are located in open areas that receive a lot of sunlight, such as deserts or rural areas.
Currently, the 530-megawatt Meridian Solar Farm in Western Australia and the 400-MW Limondale Solar Farm in New South Wales are two of the largest solar farms in Australia.
2. Community Solar Farms
Community solar farms are smaller and more localised. They produce between 100 kilowatts (kW) and 5 megawatts (MW). Community solar farms are small-scale solar farms owned by the community and usually financed by the government. Electricity produced by community solar farms is sold to electric companies.
Customers of that power company can then adjust their electricity bills based on the power output generated by the community solar panels, thereby reducing their electricity bills by a certain percentage.
The Repower Shoalhaven Community Solar Farm in New South Wales is an excellent example of a community solar farm.
Other Solar Farm Types in Australia
There are many solar farm designs in Australia, each with pros and cons. Below are the different types of solar farms.
3. Distributed Solar Farms
Solar farms typically require large tracts of land. But the land is limited and therefore expensive. One solution is to dismantle solar farms and move them to consumers. For example, installing a rooftop solar system can save on land, infrastructure, and conversion needs.
Therefore, distributed solar farms, also called rooftop solar farms, can be used for commercial and residential buildings. More than 2.7 million homes in Australia have solar panels installed on their roofs.
4. Hybrid Solar Farms
Combined Renewable Energy Systems (CRES) combine solar farms with wind or battery storage to create a more stable, reliable power supply. An example is the Kennedy Energy Park in North Queensland, which combines a 43 MW solar farm, a 21 MW wind farm, and a 2 MW battery storage system.
5. Floating Solar Farms
Floating solar farms are solar farms that float on large bodies of water. Typically, installers will place solar panels on water surfaces such as lakes, ponds, oceans, seas and reservoirs. Since 70% of the Earth's surface is covered by water, floating solar farms can fully use Australia's water resources.
In addition to reducing evaporation rates and improving water quality, floating solar farms can provide renewable energy to nearby communities or industries. Australia's first 100kW floating solar farm was completed at Godley Reservoir in Adelaide in 2018.
6. Agricultural Photovoltaic Solar Farms
Combining agriculture (growing crops and raising animals) with solar technology (using the sun to generate electricity) creates an agricultural photovoltaic solar farm. In other words, agricultural photovoltaic solar farms combine agriculture with solar energy production.
Agriculture can reduce the cost of maintaining solar farms, and solar panels can provide shade and protection for crops or livestock. While this type of solar farm is still in its infancy in Australia, it is expected to grow in popularity as the land gets smaller.
How Much Does It Cost To Build a Solar Farm?
The total cost of building a solar farm in Australia varies widely and is affected by several variables. Typically, factors that affect the price of solar farms include the scale of the project, solar panels, inverters, labour, and grid connection infrastructure.

However, on average, the current cost of building a utility-scale solar farm in Australia is between $1.2 million and $1.5 million per megawatt (MW) installed capacity. Due to their smaller size, smaller plants may be less efficient than utility-scale solar farms.
Therefore, the total cost of building a 100 MW solar farm will be between $120 million and $150 million. The table below shows the cost and payback time of a 1 MW solar farm in different countries.
|
Country |
Cost |
Return Time |
|
Australia |
$0.74 – $1.1 million |
5-7 years |
|
Brazil |
$0.8 – $1 million |
5-8 years |
|
India |
$0.55 – $0.68 |
5-8 years |
|
Spain |
$0.88 – $1.1 million |
7-10 years |
|
United States |
$1 – $1.5 million |
7-10 years |
|
Germany |
$0.88– $1.1 million |
10-15 years |
|
Poland |
$0.88 – $1.13 million |
10-15 years |
|
United Kingdom |
$1.1 – $1.4 million |
10-15 years |
(Data Source: howtostoreelectricity)
Despite the enormous initial investment, solar farms have low operating costs and are a sustainable energy source that has the potential to pay back in the long term. The payback period for building a solar farm in Australia is approximately 5-7 years, taking into account government incentives such as the SRES and LRET.
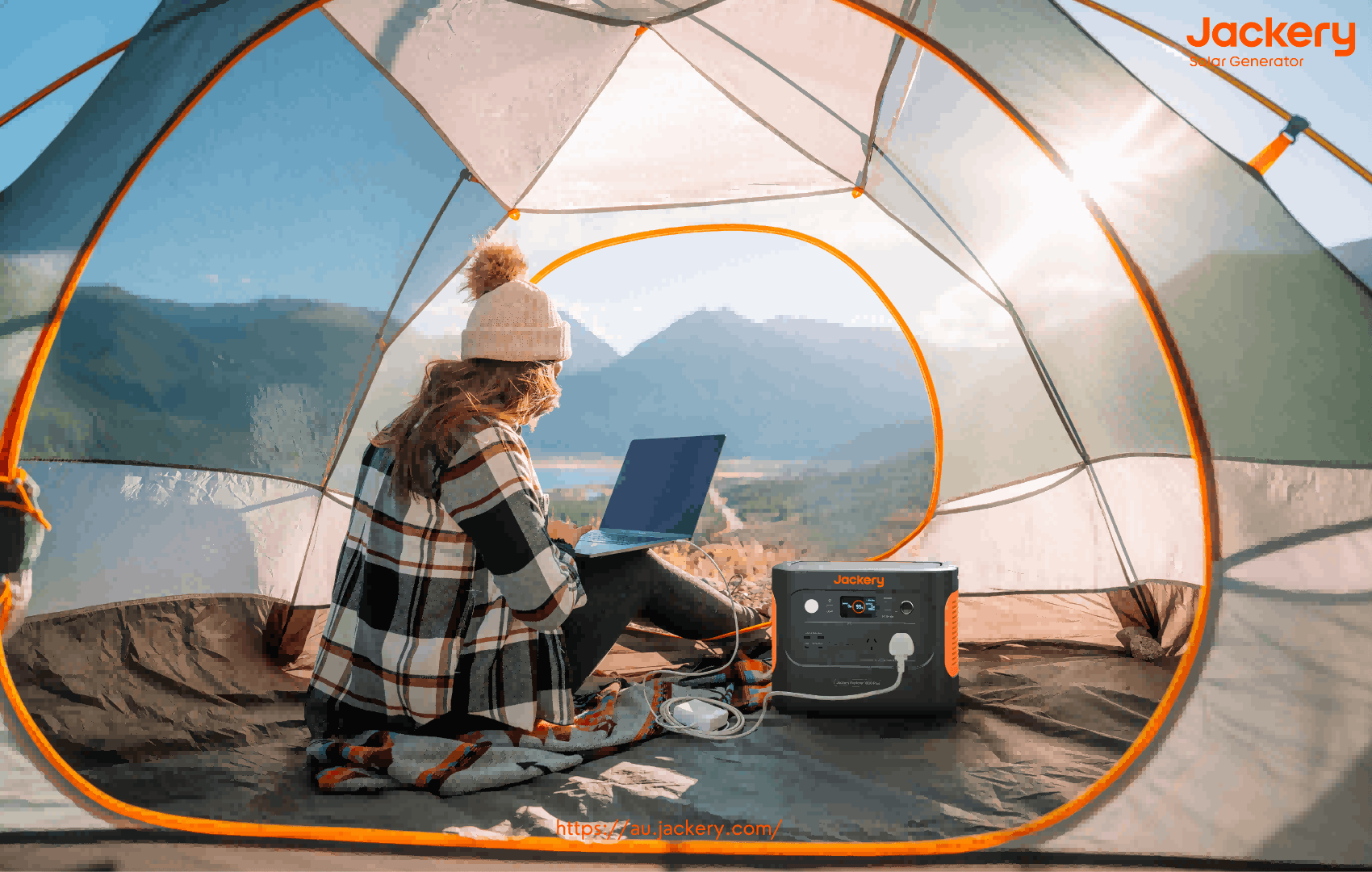
Jackery Solar Generators Explained
Australia is ideally situated for renewable energy solutions due to its sunny environment, and solar farms are spearheading the transition to a sustainable future.
Although we discuss the benefits of a solar farm in Australia, there are drawbacks, such as high initial investment costs, intermittent energy production due to weather fluctuations, extensive land use requirements that affect agriculture and ecosystems, and more. So, if you want to try solar energy, we suggest you own a solar generator.

Jackery Solar Generators offer a dependable, environmentally responsible choice for people looking to incorporate that energy into their personal or business lives. Whether working remotely in rural areas or wanting a portable backup power source, Jackery Solar Generators ensure access to clean energy wherever you go.
|
|
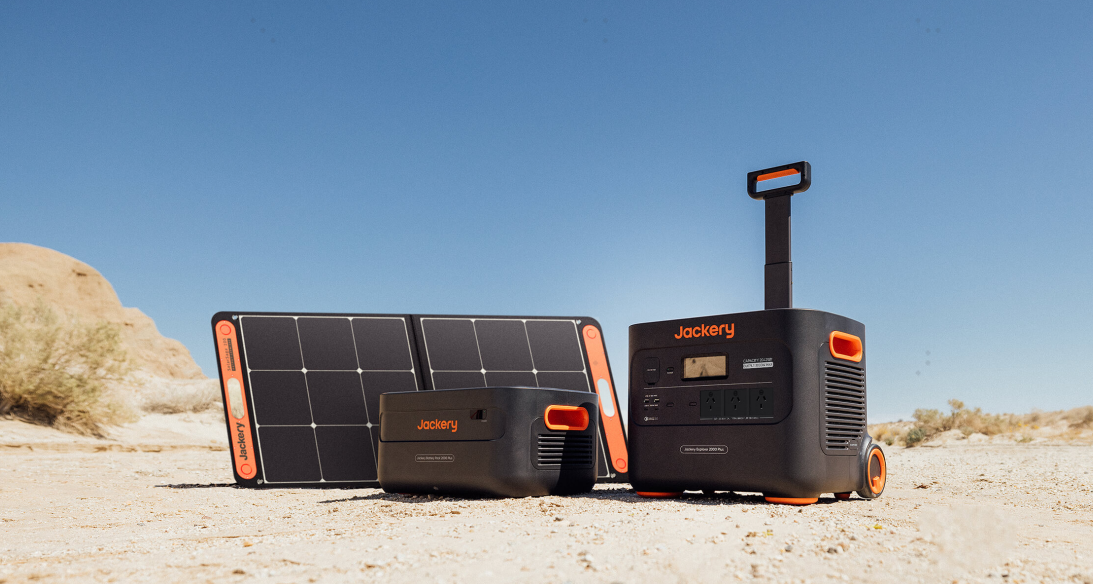
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus |
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Pro |
|
Capacity |
2042.8Wh (13A/638.4Ah) |
1002Wh (43.2V, 23.2Ah) |
|
Life Cycle |
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity |
1000 cycles to 80%+ capacity |
|
Battery Cell |
LiFePO4 battery |
Lithium-ion |
|
Dimension |
37.36x35.94x47.3cm |
25.5x26.2x34cm |
|
Recharging Methods |
Explorer 2000 Plus + 6*SolarSaga 100W: 6H; AC Adapter: 1.7H; 12V Car Adapter: 25H |
Explorer 1000 Pro + 2*SolarSaga 80W: 9H; AC Adapter: 1.8H; 12V Car Adapter: 12H |
|
Output Ports |
3*AC Output: 230V~ 50Hz, 3000W Max, 6000W surge peak; 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 15V, 12V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A |
2*AC Output: 230V, 1000W (peak 2000W); 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0x2, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 12V, 15V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A |
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
A shining example of dependability and creativity in environmentally friendly power solutions is the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus. This powerhouse, designed to meet Australian dairy farms' strength requirements, has a fantastic capacity range of 2 kWh to 12 kWh and can be expanded to meet future needs.

This solar generator is a wise long-term investment because of its exceptional LiFePO4 battery, which promises a ten-year lifespan, and its quick solar charging capabilities of only two hours. The integrated LiFePO4 battery technology ensures a long-lasting, reliable energy source with up to 4000 cycles, and the ChargeShield technology provides 62 layers of protection to safeguard your devices.
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus offers sustainability, harmony, and power. Its long-term advantages guarantee a consistent strength supply for many years, and its price makes it a wise financial decision. This solar solution embodies Jackery's dedication to dependability and environmental concern, enabling farmers to embrace a more environmentally friendly future.
Whisper-quiet and emission-free, this solar generator is the perfect way to generate clean, renewable energy without noise or environmental impact. It is ideal for your home or outdoor adventures. If you want to reduce your electric bill significantly, the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus is an intelligent investment for sustainable living in Australia.
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus
Discover the strength and adaptability of the Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus, intended to increase your energy independence. This portable generator's amazing 2000W output and sturdy 1264Wh capacity power 99% of equipment, making camping, emergencies, and off-grid adventures easier.

Because of its expandable design, you can connect up to three additional battery packs, increasing its capacity to an incredible 5kWh, sufficient for one to three days of backup power at home.
With four SolarSaga 100W solar panels, the Solar Generator 1000 Plus uses Advanced IBC Technology to deliver ultra-fast solar charging in as little as 4.5 hours, guaranteeing stay powered up even in remote areas. Its LiFePO4 battery cells provide longevity, with 4,000 charge cycles and ten years of dependable performance.
Take control with the Jackery App, which offers real-time monitoring and customisation through WiFi or Bluetooth. Compact, efficient, and built to last, the Jackery 1000 Plus is backed by a 3+2 year warranty, ensuring peace of mind as you embrace sustainable energy solutions.
How to Start a Solar Farm in Australia?
Starting a solar farm in Australia can be a difficult and expensive process. It requires careful consideration, a thorough understanding of the legal environment and effective project management. Consulting with legal advisors, environmental consultants, and financial analysts is best for in-depth knowledge about solar farms. There are several key factors to consider before investing in a solar farm.
|
Questions to Ask Before Starting a Solar Farm |
|
-How much do you need to invest? -How much do solar panels cost per acre? -What are the laws and regulations related to solar farms? -What is the return on investment in solar farms? -What problems may you encounter? |
Feasibility Study
A feasibility study can help you decide if your land is suitable for building a solar farm and worth the investment. Land evaluation should consider factors such as solar radiation, land size, and land availability. It is also essential to consider the costs of equipment, installation, and maintenance and the income you can earn from selling electricity to the grid.
Financing
First, you must determine the total capital cost of building a solar farm, including equipment, construction, and operating costs. Then, you should carefully consider sources of financing, such as grants, loans, or government incentives for renewable energy projects.
Design and Planning
Select the type and model of solar panels and inverters and plan the layout of the solar farm. Working with experienced solar engineers and contractors is essential to ensure the design is efficient and cost-effective.
Obtaining Permits and Approvals
Researching and understanding your state's laws and permitting requirements is essential before obtaining permits and approvals:
You should apply for planning permission from your local council or government department.
Comply with environmental laws and get the necessary permits.You must reach a connection and power distribution agreement with the local grid operator.
Construction
The construction of a solar farm includes the installation of equipment, connection to the grid, and system commissioning. Cooperating with an experienced contractor ensures that the installation meets the safety and reliability of the solar farms.
Grid Connection
After completing the connection with the local grid according to the agreement, the completed solar farm will be tested and debugged to ensure efficient operation of the completed solar farm.
Solar Farms in Australia FAQs
The following are the frequently asked questions about solar farms in Australia.
1. How many solar farms are there in Australia? Which state has the most solar farms?
Australia has many solar farms, but exact numbers are hard to pinpoint. However, large solar farms will account for 15.9% of Australia's renewable energy generation in 2023. Queensland currently has the most solar farms. There's a reason Queensland is called the Sunshine State. Queensland is preparing a 1,500MW sizeable solar farm project, which is expected to be one of the largest solar farms in the world when completed.
2. How big is a 1MW solar farm? How many solar panels will it have?
A 1MW solar farm usually occupies 2-3 hectares of land. Depending on the farm's capacity, the number of solar panels in a solar farm ranges from a few thousand to millions. As a rough estimate, a 1MW solar farm requires about 3,000 to 4,000 solar panels.
3. What are the disadvantages of solar farms?
Although solar farms have many advantages, there are also some potential disadvantages.
Solar farms usually take up a lot of land.
Solar farms are too dependent on sunlight. Rainy weather and other factors can limit their power generation capacity.
Solar farms may destroy the natural habitat of local animals.
Solar farms may make a lot of noise when they are in operation.
Solar farms have relatively expensive upfront costs.
4. How to choose the best location for a solar farm?
Several factors determine the best location for building a solar farm in Australia: the amount of sunlight, the cost of land, and the distance to the transmission infrastructure.
The available sunlight is the main factor in determining where to build a solar farm. Solar farms perform best in sunny climates. Geographic location impacts land prices; urban land is generally more expensive than rural land.
It is crucial to Choose a location where transmission lines are already laid or can be easily connected to the grid. These facilities must be connected to the existing grid to transmit the electricity solar farms produce to consumers.
Final Thoughts
As Australia works towards 82% renewable energy by 2030, solar farms have become an essential part of the equation. Australia's investment in solar farms demonstrates the country's commitment to renewable energy and sustainable practices.
Solar farms in Australia reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve environmental quality, deliver clean energy to remote areas, and increase grid reliability. They also create many jobs and can meet more of Australia's electricity needs.