|
Key Takeaways: |
|
• This guide delves into the fundamental principles, operations, and components of DIY solar systems, providing readers with a solid understanding of their work. • There are advantages and disadvantages to DIY solar systems. Off-grid living is ideal for DIY solar, which is inexpensive and effective at powering appliances. However, a DIY solar system may only be appropriate for some larger households. • Here's a step-by-step guide for assembling and installing a DIY solar system, covering sizing, component selection, installation, and post-installation maintenance. • The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Pro and 2000 Plus are introduced as an option for portable solar systems, offering a practical solution for individuals who require portable or supplemental solar power. A popular question is addressed: what size solar generator does an individual need? |
Can You DIY Solar System Yourself?
According to research, the average cost of going solar for homes (after accounting for the tax credit) is approximately $20,500 in 2023. Design and installation labour costs account for about 10% of the entire bill; this is what a DIY solar system will save you, as you will still have to purchase the equipment and components yourself. Regardless, it's tempting to consider DIY solar system installation to save money and have complete control over your home renewable energy project.
What is a DIY Solar System?
A DIY solar system is one that a homeowner designs, installs, and maintains themselves rather than hiring a professional installer. This do-it-yourself approach to solar energy is popular due to its low cost, customizability, and increased interest in sustainable living. In this guide, we'll look at the components of a DIY solar system, such as panels, batteries, and inverters, and the fundamentals of using solar energy at home.
A DIY solar system is a complete, unified set of components that form a functional solar panel system. While each DIY solar system will be unique, it should include everything you need to gather, store, convert, and transport the sun's energy into useful power for your home or RV. All DIY solar system components may often be purchased separately and combined into a solar panel system. A solar system, on the other hand, is designed with advanced preparation. The user does not need to determine whether the components are compatible; assembly is seamless, and compatibility is ensured.
What Are The Components of A DIY Solar System?
Although some solar kits may have more items than those listed here, any solar kit worth your money will include the following:

Solar Panels: Solar panels, commonly known as PV panels, are the essential components of a solar system. The photovoltaic effect allows them to turn sunlight into power. Based on efficiency, available space, and affordability, DIY enthusiasts can select from various solar panels, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels.
Batteries: Solar batteries store the electricity produced by solar panels for later use, mainly when there is no sunlight. Lead-acid, lithium-ion, and salt-water batteries are some of the most common solar batteries. DIY solar system designers must consider battery storage capacity, voltage, and longevity to meet their energy requirements.
Inverter & Charge Controller: Inverters convert the DC generated by solar panels into AC, which most household appliances use. Several types of inverters include string inverters, microinverters, and power optimisers. DIY solar system enthusiasts should select an inverter that corresponds to the size and layout of their solar panel system. The charge controller keeps the battery from overcharging by controlling the flow of electricity between the solar panels and the battery. The charge controller is an optional component, much like the battery bank.
Cables & Wires: All DIY solar systems contain all the cords required to connect the components. Larger solar panel kits for residences will include gear to put the panels on the roof or the ground.
DIY solar systems allow individuals to control their energy generation, increasing sustainability and lowering reliance on traditional energy sources. Understanding solar system fundamentals and adhering to installation and maintenance best practices are critical to a successful, efficient DIY solar project.
What Are The Pros and Cons of A DIY Solar System?
DIY solar systems can be a good choice for moving off the grid and some small-scale household applications. However, hiring a professional installer to power your complete home may be advisable.
Most home DIY all-in-one solar systems (including solar batteries and inverters) are intended for off-grid use. Thus, you cannot utilise them while remaining connected to your utility. If you're an average homeowner, going off-grid is generally not in your best interests; connection to utility-generated electricity is required if your solar array needs to create more electricity to suit your needs at all times of the day and year.
On the other hand, home solar systems can be an effective alternative if you intend to power only some of your home. RVs, boats, and the increasingly popular tiny houses are all great places to experiment with DIY solar because they are already off-grid and transportable. Storage kits, including battery banks and systems, are also an excellent backup alternative in a power outage.
On a related note, DIY solar projects can be helpful if you have a vast property and want to power a remote place, such as a barn or tool shed, or if you're going to add outdoor lights quickly. In those circumstances, your electricity demands will be low, making purchasing and installing a small home solar kit possible.
|
Pros of DIY Solar System |
Cons of Solar System |
|
Homeowners have greater energy independence by not being connected to the electrical grid. |
Requires significantly more maintenance than would be covered by an installation warranty. |
|
Allows homeowners to save around 10% on the total cost of installation, which would otherwise be spent on labour. |
Individuals without the skills and experience of a professional installer may find it challenging to install a complete home. |
|
Practical for powering a limited number of appliances, such as in RVs or boats. |
Depending on local zoning restrictions, DIY installation may be unlawful where you reside. |
How to DIY Solar System?
The popularity of DIY solar panel systems has grown in recent years, particularly in areas with abundant sunshine, such as Australia. Using solar energy at home promotes environmental sustainability and lowers electricity expenses. However, establishing a DIY solar system involves meticulous planning and consideration of numerous elements.

Step 1: Size Your System via Power Consumption
When designing a solar power system, you must first determine the size of the system required. This size is primarily determined by the electricity needed to power all appliances. Conduct a thorough energy audit to assess your energy use to size your system correctly. A straightforward approach is to look at your previous electricity bills and compute your average daily electricity consumption to select the entire number of watts needed for your solar system.
Begin by identifying the equipment you intend to power with your solar generator. Take note of each gadget's wattage, usually indicated on the item or in the instructions. Add these wattages together to calculate the total wattage. Determine how many hours every day each gadget generally operates. To calculate the watt-hours (Wh) required for each gadget, multiply its wattage by the number of hours used. Add the Watt-hours necessary for all devices to calculate overall daily energy consumption.

Step 2: Obtain Necessary Permits in Your Region
You'll need to secure the proper permits, as different regions have different regulations for solar installations, so contact your local building department to learn more about the procedure and submit the required documentation.
Most property owners require many permits to construct and connect their solar panel systems to the grid (including DIY solar projects). Exceptions are rare. One example is an off-grid solar energy installation. However, it is inconclusive; some states and towns may require you to obtain specific licences even if you are going off-grid. Solar permit requirements vary by region, municipal code regulations, and the size/type of your solar installation. The most typically required solar permits are:
- An electrical permit
- An interconnection permit to connect to the grid
- A building permit
- A solar photovoltaic (PV) permit
Your local building authority and utility company will need information about your system to obtain permits. Your local utility company issues you the connection permit. During the application review process, your solar system's compatibility with the grid is routinely verified, as is the safety and stability of your house's electrical network.
Step 3: Purchase The Installation Tools & Materials
Solar panels, batteries, charge controllers, solar power inverters, and various installation tools are required for any solar system project. You may compare panel, battery, and inverter products based on efficiency, warranty, and other specifications.
Cable size is not a significant consideration for tiny systems like the one we are constructing. You may use a standard 4 mm cable for all your connections. Proper cable diameters ensure safety and optimal performance for more extensive systems. In that case, be careful to consult an online cable sizing guide.
- Solar panelkit: Solar panel kits typically contain panels, an inverter, and mounting tools.
- Drill and drill bits: Use drill bits for installing panels and brackets.
- Screwdriver set: Screwdriver set for assembling and fastening components.
- Wire strippers and crimping toolsfor electrical connections.
- Multimeter: Use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, and resistance during installation.
- Safety belts: Safety belts are essential during roof installations.
- Gloves and safety glasses: Use gloves to protect hands and eyes during installation.
- Wiring: comprises solar cables and connections.
- Mounting brackets: Suitablefor roof or ground installations.
- Weatherproofing materials: include sealants and grommets to safeguard electrical connections.
Step 4: Install The Solar System
Solar is growing increasingly popular among homeowners and travellers, and it's easy to see why. Going solar requires a lot of effort, from navigating technology alternatives to dealing with permitting. However, with an increasing number of solar panel kits available, going solar alone has always been challenging. By this time, you'll have all of the correct equipment sizes. This gets you to the final step: installation. Installing a solar power system is straightforward.
Site Assessment: First, evaluate the insolation, location, and structural integrity of the installation site (often the roof) to identify the optimal orientation and angle for maximum solar gain. In the southern hemisphere, this would be a northward direction.
Mounting the Solar Panels: Install the mounting brackets and rails on the roof, ensuring they are securely secured, and then position the solar panels on the rails and secure them with clips. For best results, arrange the solar panels neatly and evenly.
Terminal Block and Inverter Installation: Use weatherproof solar connectors and cables to connect the solar panels. Then, build a solar inverter to convert the solar panels' DC power to AC power. The inverter can be linked to solar batteries to form a complete energy solution.
Battery System Integration: You can connect it to your inverter and solar panels if you need more storage. The Jackery Solar Generator has a built-in battery, making it a straightforward energy storage and management solution. You must configure the solar system settings, which include the inverter output and battery charge/discharge restrictions. In addition, the Jackery Solar Generator offers an easy-to-use interface for monitoring energy use and power distribution.
Step 5: Post-Installation Check & Maintenance
After installing your panel and system, schedule an inspection with the local construction authority closest to you. This ensures that your system conforms with local regulations. Once you have passed this inspection, you can apply to connect to the grid. The local utility company will provide a meter to record your power exports.
System Testing: You should thoroughly test the complete solar system, including the solar panels, inverter, and connection to the local utility. Check for any problems and ensure that all components are working correctly. Then, check the system's performance using the inverter's built-in capabilities and the utility metre. Finally, periodic checks on energy output, efficiency, and battery capacity exist.
Fine-tuning The System: You can make any necessary changes to the angle of the solar panels or the system settings to improve performance and guarantee that the DIY solar system is configured correctly to fulfil energy demands.
Commissioning: Once you're pleased with the configuration, formally commission the system and record all system characteristics to ensure they satisfy the design standards.
You can build a comprehensive solar panel system with these detailed instructions for better energy storage and management. This strategy offers a versatile and practical option for capturing solar energy, ensuring reliable backup power, and increasing the usage of renewable energy.

If you think a DIY solar system is too complicated for you but still want to attempt a sustainable lifestyle, consider the Jackery Solar Generator, which combines solar panels with a portable power station to convert sunlight to electricity. For the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Pro model, ensure that it matches the system output; for the Solar Generator 2000 Plus, consider the higher power output for larger installations. The Jackery device can be utilised as a portable power storage and backup system for the energy supplied by the solar panels.
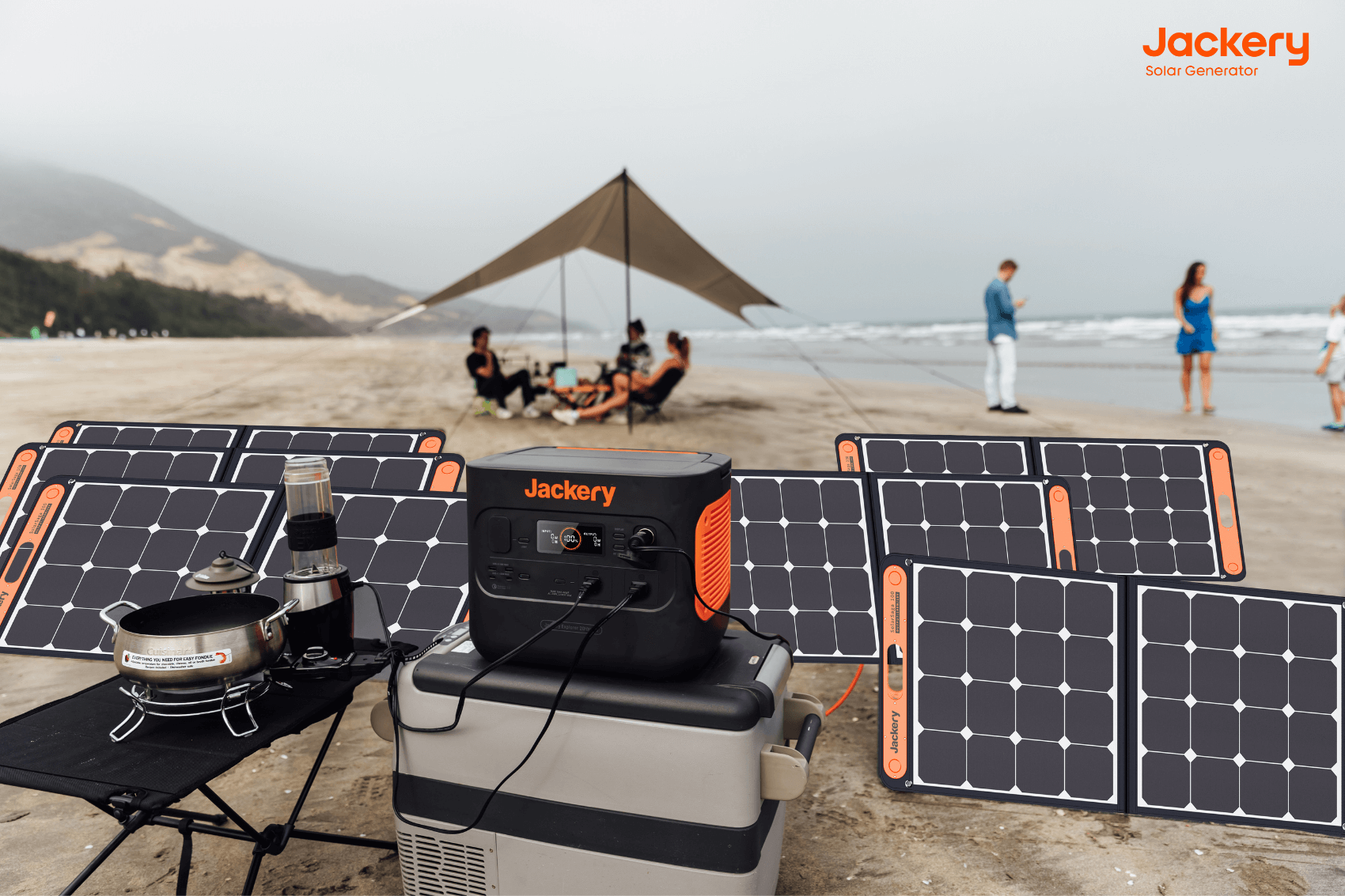
Jackery Solar Generators: Portable Solar Systems
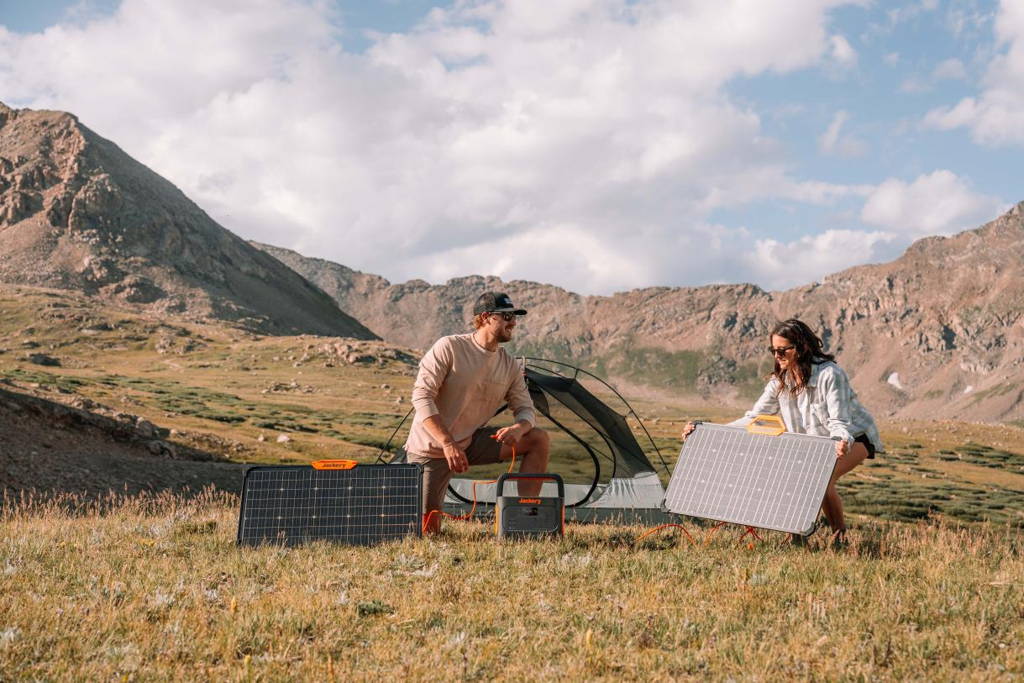
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Pro and 2000 Plus work perfectly with the DIY solar setup. The Jackery Portable Power Stations serve as a central power storage device for the energy produced by solar panels. While these devices are designed for Jackery SolarSaga solar panels, they are also compatible with other panels, allowing you to create personalised DIY solar systems. These generators provide dependable backup power to ensure energy supply during a power loss or off-grid operation. Users can expand the system by adding more solar panels or incorporating more Jackery battery packs, increasing the system's capacity and reliability.
Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Pro
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Pro is a powerful portable power station suitable for various applications. It has a sleek, modern appearance and sturdy build quality, making it perfect for indoor and outdoor use. Solar power can recharge the generator in less than 2 hours, making it handy when power is rapidly replaced.
With a 2160Wh battery capacity and a 2200W inverter (instantaneous peak up to 4400W), it can offer reliable power to various appliances and equipment. Furthermore, it is claimed that this product can survive for more than ten years under typical use, demonstrating its exceptional durability and reliability. This system supports SolarSaga 100W solar panels and AC charging, giving users various options. In addition, it incorporates an effective battery management system (BMS) to ensure user safety. Despite its high capacity, it is meant to be small and lightweight, making it easy to transport and relocate.

Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus
Jackery's high-performance Solar Generator 2000 Plus significantly advances portable power solutions. With its large capacity and high power output, it can power conventional vans for weeks and suit outdoor adventures or home backup power supply. Incorporating battery cells into the Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus significantly boosts capacity from 2 kWh to 12 kWh, resulting in a paradigm shift in domestic backup power supply.
The Explorer 2000 Plus can extend to 3000W and has a 30% higher rated power than comparable 2 kWh items. Powered gadgets make up the vast bulk of essential domestic appliances. Despite its steady daily use, the Solar Generator 2000 Plus can be fully charged in 6 hours (with 6 SolarSaga 100W solar panels). The power source becomes self-sufficient, charging using solar energy rather than the power grid.

What Size of Solar Generator Do I Need?
To choose the right size solar generator for your needs, examine your energy requirements, the efficiency of your solar panels, battery storage capacity, and the specific needs of your equipment. Choosing the appropriate size solar generator necessitates balancing energy requirements, setup efficiency, and practical issues such as portability and cost. Consumers can choose a Jackery Solar Generator with capacities ranging from 12 kWh to 300Wh for a portable solar system based on their energy needs. The formula for calculating the operational hours of appliances powered by Jackery Solar Generators is as follows:
Working Hours (H) = [Jackery Solar Generator Capacity (Wh)*0.85] / Appliance's Wattage (W)
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus can power a 100W ceiling fan for 17 hours (2042.8Wh x 0.85/300). This calculation helps determine the hours when appliances can operate.
DIY Solar System in Australia FAQs
The following are the most frequently asked questions about DIY solar systems in Australia in Australia:
- Can I claim solar panels on tax in Australia?
As a capital asset, solar depreciates over time. If eligible, your company can write off the asset's cost over a defined length of time determined by the Australian Tax Office. A solar system has a practical life of twenty years.
- Is DIY solar worth it?
DIY solar systems may be appealing to install, but their long-term value is debatable due to quality alone. A solar panel system should typically generate power for 25 to 35 years, so investing in high-quality equipment and a reliable contractor is critical. If you buy a home solar system kit from a merchant, you can pay less per watt. However, you will receive a different efficiency or quality than professional installers often provide with their products.
Assuming you do the entire thing yourself (no contractors for any of the chores), the overall cost of a 5 kW DIY solar project ranges between $5,000 and $7,500. Choosing DIY over a professional solar installation might save you $7,250 to $9,759.
- How many batteries do I need for a 10kW solar system?
A 10kW solar system typically requires a 20-30kWh battery bank, which can range from 100 to 150 batteries with a capacity of 200Ah apiece. However, you should check with a specialist to calculate the exact amount of batteries needed for your particular solar power system.
- How do you size a DIY solar system?
To calculate how many solar panels you need, multiply your household's hourly energy need by the peak sunlight hours in your area and divide by the wattage of each panel. Use a low-wattage (150 W) and high-wattage (370 W) example to determine a range.
Final Thoughts
To summarise, the rise of DIY solar systems in Australia indicates a shift towards renewable energy alternatives. Achieving a sustainable future necessitates overcoming obstacles, embracing technological advances, and making conscious choices about energy consumption. The Jackery Solar Generator is a beacon of innovation on this journey, providing practical solutions for those committed to positively impacting the environment and their energy footprint.