Have you ever wondered what all the numbers and ratings on a battery represent as they become increasingly common? As you go through battery listings online, you'll notice that batteries are described in various ways. The terms "amp hours," "cycles," "cold cranking amps," and other terms are used to define the sort of battery you are purchasing.
If you are unfamiliar with these words, you should learn what they imply before purchasing to receive the correct battery for your application. We have a brief and easy explanation to help you understand what Ah means on a battery, what ampere-hour is, how to read Ah values, and the distinctions between Wh and Ah. Furthermore, Jackery Portable Power Stations with more extensive Ah ratings are ideal for using solar energy to power indoor and outdoor appliances.
Amperage can be defined as the volume of electrical current. Volts are the units of measurement for the quantity of energy supplied to an electrical circuit. The watt is the most familiar of all the numerous units of electricity.
Ah is the energy stored in a battery sufficient to facilitate the passage of one ampere of current for one hour.
The ampere-hour is calculated by combining the current and the time required for a battery to discharge completely.
The battery capacity is denoted in Ah, which stands for amp-hours.
We highly recommend Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus, 1000 Pro, and 600 Plus portable power stations with higher Ah.
The pace at which electrons flow through a wire or item is measured by amperage, also known as electric current. This rapid movement is analogous to water flowing through a canal or canyon. The higher the amperage, the more electrons are traveling.
Amperage can be defined as the volume of electrical current. It is a critical indicator of how much energy an electric device or system can transport. A bulb, for example, consumes less current when it glows poorly, whereas it consumes more current when it shines brilliantly. Before delving into AH in a battery, we must first grasp the fundamental concepts of voltage, current, power, etc.
Volts are the units of measurement for the quantity of energy supplied to an electrical circuit. A circuit is a term used to describe an electronic equipment. Twelve volts are always "given" to a 12V gadget by the battery. The voltage of a battery is permanently fixed (e.g., 12, 24, or 36 volts), whereas the voltage of a device is always in a constant range. A gadget that operates on 12 volts, for example, requires a battery that also works on 12 volts.
Wattage is the most familiar of all the numerous units of electricity. Wattage is the amount of power consumed by an electric gadget. Power is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the number of amps (Watts = Amps x Volts). It is the quantity of energy a device utilizes, thus, an indicator of its power. As the amount of amps increases, so does this.
What Is An Ampere-Hour (Ah)?
Simply comprehending Ah makes it straightforward to determine what Ah means on a battery. Ampere hours, also denoted as Ah or amp hours, refer to the quantity of energy stored in a battery sufficient to facilitate the passage of one ampere of current for one hour. An alternative formulation would be to define 1 Ah as the capacity of a battery to supply amperage for one hour. Determining the power of an energy storage device, such as a deep-cycle battery or rechargeable battery, is facilitated by this unit.
Ampere-Hour (Ah) = Ampere (A) x Hour (H)
Typically, large batteries are quantified in ampere-hours. On the contrary, the rating for tiny batteries such as personal vaporizers and notebook computers, as well as standard AA and AAA batteries, is expressed in milliampere hours (mAh). A minimum 4Ah capacity is typically indicated conspicuously on a battery, similar to the 5Ah capacity depicted in the image.
What Is Milliampere Hour?
One-thousandth of one Ah is one mAh. Like ampere-hours, milliampere hours denote the quantity of current that a battery dissipates within a single hour and provide insight into the battery's remaining operational time before requiring recharging. Typically, a more excellent milliampere hour value signifies an extended duration of battery operation, an increased capacity for storage, or both. A milliampere-hour rating represents an extended operational duration instead of an increased velocity.
Although the general public knows that AC and DC are two distinct current forms, only some are aware of their distinction. Direct current (DC) refers to a unidirectional passage of electric charge that is constant in magnitude. In contrast, alternating current (AC) changes direction at a predetermined rate of sixty per second.
Always, batteries are DC. For this reason, both a positive and negative terminal exist. Constant current will flow from one terminal to another via the appliance while being powered. With modification, electrical devices are designed to operate on AC or DC power.
What Does Ah Mean On A Battery?
So, what does Ah mean by a battery? The unit of measurement for the rate of electron flux or current in an electrical conductor is the ampere. The energy charge of a battery in amp-hours is defined as the quantity of charge required to permit the passage of one Amp of current for one hour.
To determine the amp hour rating (AH) of lead-acid batteries, manufacturers discharge the batteries to 0% capacity within a specified period. The Ah rating represents the amperage required to deplete the lead-acid batteries to zero over that time.
Twenty hours is the standard amp-hour rating for deep cycle batteries, considerably less than the average amp-hour rating of seventy hours for a car battery. Therefore, if your battery has a rating of 100AH @ 20Hr rate, it has been exhausted for 20 hours at a 5 amp load, exceeding its deep cycle capacity.
As lithium batteries (not rechargeable) and lithium-ion batteries (rechargeable) have a current rating of 3,200 mAh, they are capable of discharging 3,200 milliamps (3.2 amps) in an hour before dying. However, starting batteries are typically rated at 10 hours per hour since they are utilized more frequently.
As the rate of use of a battery increases, so does its mAh rating. The phenomenon whereby batteries deplete more rapidly and exhibit a reduction in total available amperage is called the Peukert effect. Frequent depletion will have a substantial impact on the battery life.
The rate of electron flux or current in an electrical conductor is denoted in amperes. A current ampere equals one coulomb of electrical charge that traverses a designated area within one second.
The ampere-hour is calculated by combining the current and the time required for a battery to discharge completely. One straightforward expression is as follows: one hour of current flow at one ampere. The charge transfer within one hour amounts to 3,600 coulombs (ampere-seconds). The battery's ampere-hour rating is visually indicated. Without a rating, the battery is typically a starting battery not intended to deliver continuous power in ampere-hours.
What Are Common Ah Ratings?
A 20-hour rate is the prevailing acknowledged ampere-hour rating time for backup power systems, which include uninterruptible power supplies, solar electric batteries, and deep-cycle batteries. The rating denotes the decline of the battery to 10.5 volts within 20 hours, during which the total ampere hours supplied are quantified.
The mAh rating of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries indicates that they can discharge 3,200 milliamps (3.2A) within a single hour. Typically, starting batteries have a 10-hour rating due to their increased use rate. A six-hour rate is frequently specified for industrial batteries, corresponding to the customary daily duty cycle. Sure batteries are designated with a 100H ampere-hour rate. Determining the battery capacity for long-term reserve ampere hours is facilitated by this.
The ampere-hour rating of lead-acid batteries, such as those found in automobiles, is established by the manufacturer through a controlled discharge process to 0% capacity within a designated time frame. The ampere-hour rating is the current required to discharge the battery to zero within that same period.
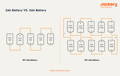
What Is The Differences of 2Ah & 5Ah Battery?
As an illustration, consider a 5-cell 18V (or 20V Max), 2Ah battery; each cell is a 3.6V, 2Ah cell (FIG 2). As a result of connecting all five in series, their voltages are summed, but not their amp-hour ratings. An 18V, 2Ah battery combines five 3.6V, 2Ah batteries in series.
Two bundles of five cells comprise the larger battery, comprising ten cells. Although the cells remain at 3.6V, their capacity has increased to 2.5Ah. After connecting each pack of five in series, the two groups are linked in parallel. Comparing cells in parallel adds their amp-hour ratings but not their voltages; this is the inverse of connecting cells in series. By combining two 18V, 2.5Ah cells in parallel, the battery is reduced to 18V, 5Ah.
Although the amp-hour rating does not directly correspond to power, the larger battery will typically provide slightly more power. This is because ten cells perform the tasks that five cells do in the smaller battery, allowing it to supply power to the instrument.
How to Calculate Ah Rating in A Battery?
The rate of electron flux or current in an electrical conductor is denoted in amperes. A current ampere equals one coulomb of electrical charge that traverses a designated area within one second. The ampere-hour is calculated by combining the current and the time required for a battery to discharge completely. In mathematical notation, Ah is denoted as follows:
Amp hour (Ah) = Current (I) x Discharge time (T)
The process of ascertaining the ampere-hour rating can be illustrated through the use of the following case study: Consider a battery that consumes 40 amps (A) and depletes within 30 minutes:
Subsequently, if the current is 30A and the discharge time is 0.5 hours (30/60), the ampere-hour should equal 15Ah/H (30A x 0.5H).
What Is Battery Capacity?
The capacity of a battery is denoted in Ah, which stands for amp-hours. As implied by its moniker, this indicates how many amps the battery can provide in an hour. For instance, a 100Ah lithium battery operating at 12V can supply 100A to a 12-volt device for one hour. A 25-ampere device could be powered for four hours with the same 100Ah battery (100/25=4). A battery with a 50Ah capacity and an operating voltage of 12 volts is designated 12V 50A. A 24V 100A battery operates at 24 volts and has 100 Ah.
Adequate capacity (the number of amp-hours the battery can deliver in actual use) and nominal capacity (the number of amp-hours the battery can produce according to specifications) are notably dissimilar.
For instance, The capacity of a battery to supply current for a specified duration is denoted in amp-hours (Ah). In contrast, a rating (typically expressed in milliampere-hours or amp-hours) approximates the time a battery can deliver a particular current.
Jackery Portable Power Stations with Higher Ah
Jackery is a widely recognized producer of superior solar products, which includes the
Jackery Portable Power Station. It is comparatively minor and up to 30% lighter than alternative options. Its ergonomic handle design facilitates portability to any location of interest. With a capacity of 240W to 2000W, Jackery's portable power solutions can supply power to 99 percent of equipment, including refrigerators, televisions, CPAP machines, lighting, and more.
One can preserve as much as 80% of the battery's maximal capacity by employing a lithium battery of superior quality that possesses a higher Ah rating. These power plants have significantly greater capabilities and can run numerous household appliances for days or hours.
Jackery Portable Power Stations supply essential appliances with consistent and dependable power via
lithium batteries. The optimal utilization of solar energy is achieved by connecting
Jackery Solar Panels to Jackery Portable Power Stations via the
Jackery Solar Generator. In addition, they utilize sophisticated BMS and pure sine wave inverters to ensure dependable and uninterrupted power delivery.
Jackery has unveiled the Explorer 2000 Plus, a cutting-edge portable power solution with exceptional performance. Thanks to its substantial capacity and formidable power output, this device can sustain the operation of standard domestic appliances for several weeks and fulfil all the power needs associated with outdoor adventure or professional activity.
Jackery Explorer 2000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 2000 Plus allows adding extra battery packs, which boosts the capacity from 2 kWh to a remarkable 12 kWh, thus enhancing the solar charging capabilities significantly. With the ability to be expanded to 3000W, this solar product offers a 30% higher rated power than other 2 kWh solar goods available in the market. Practically all essential household equipment is energised.
The
Explorer 2000 Plus is an industry's pioneering add-on battery pack that can be recharged using solar panels. This feature enhances versatility, improves charging efficiency, and reduces charging time. The
LiFePO4 battery, with its sophisticated technology, guarantees a lifespan of 10 years, even with daily usage limited to once per day. Jackery solar panels generate more energy over their lifespan due to their exceptional solar conversion efficiency, reaching up to 25%.
Explorer 2000 Plus Portable Power Station
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity
Explorer 2000 Plus + 6*SolarSaga 100W: 6H; AC Adapter: 1.7H;
12V Car Adapter: 25H
3*AC Output: 230V~ 50Hz, 3000W Max, 6000W surge peak; 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 15V, 12V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A
TV(200W): 8.4H
Refrigerator(700W): 2.4H
Microwave(750W): 2.2H
Coffee Maker(800W): 2.1H
Blender(300W): 5.6H
Stove(850W): 2H
Numerous devices can be powered simultaneously by the Jackery Explorer 1000 Pro Portable Power Station, which features an entirely compatible power station. During camping excursions and power disruptions, the 1000w portable power station's 1002Wh battery capacity ensures that your electrical devices are always charged. It weighs only 11.5kg and features an industry-leading BMS, 94V-0 fire-grade material,
pure sine wave technology, and a collapsible handle.
Jackery Explorer 1000 Pro
One DC vehicle port, two USB A connectors, and two 1000W AC output receptacles are included on the Explorer 1000 Pro portable power station. It can provide power to as many as 93% of your household appliances, including your computer, electric radio, refrigerator, and phone. For instance, it can power a 200W computer for four hours in an emergency, which is adequate for work or other purposes. For eight hours, it can also operate a 100W CPAP machine.
The foldable handle facilitates storage and transportation. This portable power source is ideal for camping excursions due to its thin construction and 1,000-charge cycle lifespan. Your electronics are supplied with consistent power by a pure sine wave inverter. An energy management system (BMS) monitors and maintains the battery life of this ultra-quiet (46dB) product.
Explorer 1000 Pro Portable Power Station
1000 cycles to 80%+ capacity
Explorer 1000 Pro + 6*SolarSaga 80W: 9H
AC Adapter: 1.8H
12V Car Adapter: 12H
2*AC Output: 230V, 1000W, peak 2000W; 2*USB-A: Quick Charge 3.0x2, 18W Max; 2*USB-C: 100W Max, (5V, 9V, 15V, 12V, 20V up to 5A); 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A
TV(200W): 4H
Fridge(500W): 1.6H
Blender(300W): 2.7H
CPAP Machine(100W): 8H
Computer(200W): 4H
Electric Wheelchair(380W): 2.1H
The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus is the best portable power option. It can power many outdoor devices, from GPS devices to camping lights, with its 800W output and 632Wh
capacity. The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus is your go-to power station for all your activities because it is strong, durable, and light. It makes charging fun things to do outside easy.
Jackery Explorer 600 Plus
The Jackery Explorer 600 Plus can meet all of your outdoor entertainment needs. A lot of different outdoor entertainment gadgets can connect to it. Its dual PD fast charging can go up to 100W, so your devices will be charged quickly. The Explorer 600 Plus can give you long-lasting power, a backup in an emergency, or quiet charging that won't bother anyone.
It's small and light (16.1 pounds/7.75 kg), making it convenient and easy to store. It's easy to take with you because the handle folds up. You can always get power to stay linked and charged on your hikes, no matter where they take you.
Explorer 600 Plus Portable Power Station
4000 cycles to 70%+ capacity
Explorer 600 Plus + SolarSaga 100W: 9.5H; AC Adapter: 7.5H;
12V Car Adapter: 7.5H
2*AC Output: 120V~ 60Hz, 6.67A; 1*USB-A: 18W Max, 5-6V⎓3A, 6-9V⎓2A, 9-12V⎓1.5A; USB-C1: 30W Max, 5V⎓3A, 9V⎓3A, 12V⎓2.5A, 15V⎓2A, 20V⎓1.5A; USB-C2: 100W Max, 5V⎓3A, 9V⎓3A, 12V⎓3A, 15V⎓3A, 20V⎓5A; 1*Carport: 12V⎓10A
Phone(10W): 53H
TV(60W): 8.9H
Fan(100W): 5.3H
Lighting(25W): 21.4H
Speaker(120W): 4.4H
Computer(200W): 2.6H
What Is The Difference Between Ah and Wh?
You should be able to calculate your energy requirements in advance and choose energy systems of the appropriate scale. Before comprehending your energy storage needs, you must distinguish between amp-hours and watt-hours.
Amp-Hour Is Current Over Time
Amp-hours (Ah) are a charge measurement. Current, or amps, must be known before calculating amp hours. Current is a stream of charged particles, including electrons and ions, in motion through an electrical conductor or void. An amp hour represents the number of amps that move in one hour. To illustrate, a battery with a capacity of 150 Ah could discharge 150 amps in a single hour or 150 Ah.
In two hours, this 150 Ah battery would discharge 300 amps, or 300 Ah. Briefly, amp hours indicate the amount of current that a battery is capable of delivering for a specified duration. To ascertain the charge and discharge rates of a battery, consult its C rating, a metric that quantifies the rate at which the battery is ultimately charged or discharged.
Watt-Hour Is Power Over Time
Watts denote power, with one watt being equivalent to one joule per second. Watt hours (Wh) are energy units utilized to quantify the capacity of power (watts) in the process of varying over time. In practice, this refers to the wattage consumed by an appliance in a single hour, such as a toaster oven or light bulb.
Multiply the wattage by the number of hours the appliance uses to determine watt-hours. To illustrate, in the case of a luminaire with a rated power of 50W and the determination of its daily power consumption in watts, the equation can be expressed as 50W multiplied by 24 hours, yielding 1200 Wh.
Are Higher Ah Ratings Mean More Power?
The answer is no. Although the Ah value does not inherently indicate a more potent battery, it can occasionally be interpreted as such. The number and density of current-supplying cells, as well as the heavier gauge of conductors and components, enable a more significant current to flow through a battery with a higher Ah value, resulting in reduced resistance.
Additionally, with a greater Ah, you can power more devices longer while putting less stress on the battery components. An increased burden will affect the battery's lifespan. It is logical to assume that a battery with a lifespan of 100 hours would deliver fewer amp hours than one with only five hours, given that the former must conserve power to endure.
Generally, amp-hour ratings are most valuable when contrasting two distinct batteries. Thus, assuming all other variables remain constant, it is evident that the battery possessing the more excellent amp hour rating will require fewer recharging pauses. From this comprehensive guide, you will learn what Ah means on a battery and how to calculate the Ah rating of a battery to assist you in selecting the appropriate battery. Additionally, the Jackery Portable Power Station is the best solar storage battery pack with a higher Ah.
Best-selling Jackery Portable Power Station